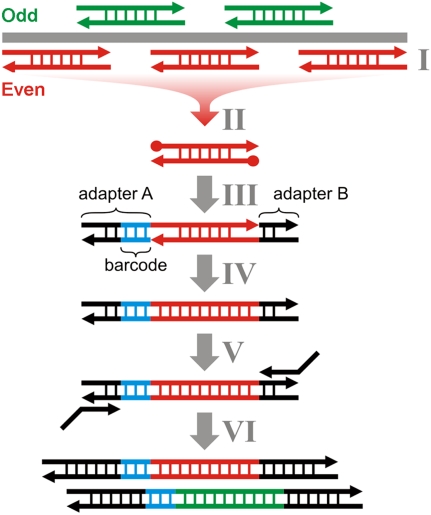
Figure 1.
Schematic description of DMPS. Multiplex PCRs with nonoverlapping primer sets (“Odd” and “Even”) are performed in plate setup (I). After removing primer dimers and other spurious amplification products by size selective purification with SPRI beads, the double-stranded PCR products are blunt end repaired (II). Two different truncated double-stranded 454-adapters (A and B), one of which is barcoded (blue), are randomly ligated to either end of the double-stranded molecules by single-stranded ligation (III). Nicks are closed using a strand-displacing polymerase (IV), and the adapters are extended to full length in an amplification step with 5′-tailed primers (V). Library molecules carrying the same adapter on both ends are excluded from amplification, because they form hairpin structures that prevent primer annealing. Regardless, such molecules would not interfere with sequencing. Double-stranded barcoded sequencing libraries from multiple PCR products are pooled in equimolar ratios (VI) and sequenced on a high-throughput platform.