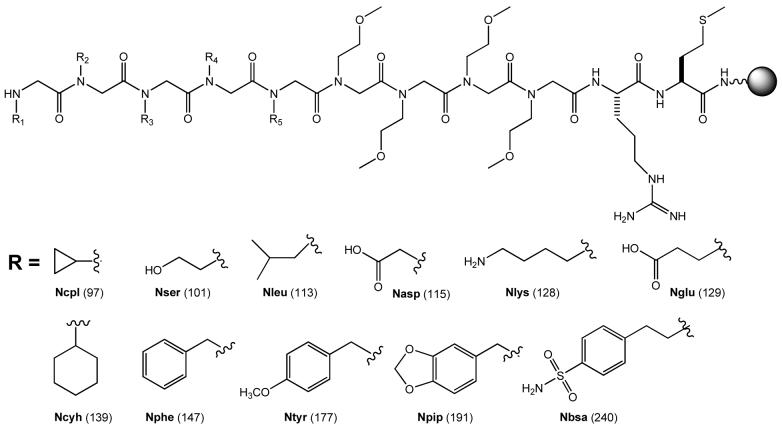
Figure 1.
The structures of peptoid library I and the building blocks used for its synthesis. The side-chain structure, the four-letter code, and the residue mass of 11 peptoid monomers are shown. Library I was constructed with 8 of the monomers (excluding Nasp, Ncyh, and Ncpl) and had a theoretical diversity 32,768. Library II contained 10 monomers (excluding Nasp) and a peptide linker, LNBBRM, with a theoretical diversity of 100,000. Library III was constructed with 7 N-substituted glycines (Nasp, Nbsa, Nleu, Nlys, Nphe, Npip, and Nser) and 3 amino acids (glycine, sarcosine, and L-proline), with the peptide linker LNBBRM and a theoretical diversity of 100,000.