Figure 1.
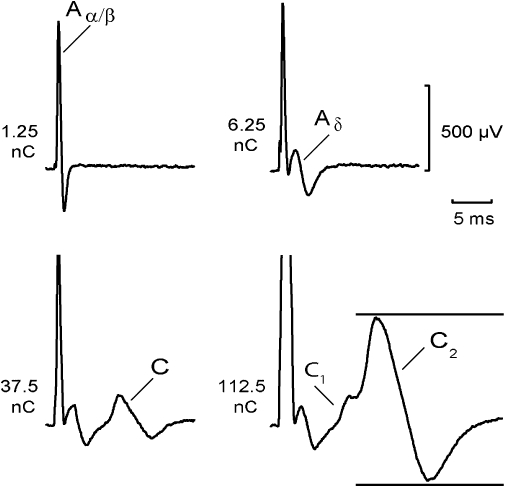
Components of the compound action potential (CAP) recorded from a segment of human sural nerve: an Aα/β peak corresponding to action potentials in large-diameter myelinated axons occurred at short latency in response to low stimulus strengths (12.5 µA, 0.1 ms). At slightly higher stimulus intensities (62.5 µA, 0.1 ms), small-diameter thinly myelinated axons were activated producing an Aδ peak at longer latency. Further increases in stimulus intensity (1 ms) activated two populations of unmyelinated axons. The fibre population contributing to the C1 peak had faster conduction velocities and lower electrical activation thresholds (37.5 µA, 1 ms) than the axonal population producing the C2 peak (112.5 µA, 1 ms). The distance between stimulus and recording electrode was 6 mm. Multiple measures of excitability were recorded by using the CAP (peak-to-peak) within the time window indicated by the horizontal bars.
