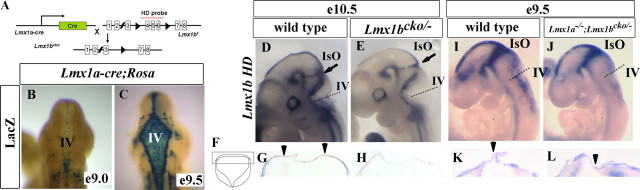
Figure 4.
A conditional knock-out strategy to delete Lmx1b only in the roof plate, where it is coexpressed with Lmx1a. A, Schematic diagram demonstrating the Lmx1b conditional knock-out strategy. Lmx1a-cre transgenic mice were bred to mice carrying a floxed allele of Lmx1b (Lmx1bf), leading to excision of Lmx1bf only within the Lmx1a expression domain in the roof plate. B, C, β-Gal activity in the progeny of Lmx1a-cre mice mated to ROSA26 floxed LacZ reporter mice. B, Only a few LacZ-positive cells are visible in the fourth ventricle at E9.0. C, LacZ expression is clearly visible at the fourth ventricle at E9.5. D–L, In situ hybridization using the Lmx1b homeodomain (HD) probe indicated in A. D, E, Whole mount at E10.5 of wild-type (D) and Lmx1bcko/− (E) embryos. Lmx1b HD expression was reduced in the fourth ventricle roof plate but remained intact in the IsO in Lmx1bcko/− embryos. F, Schematic of a transverse section of the fourth ventricle at E10.5. The boxed region indicates the equivalent region in G, H, K, and L. G, H, Transverse sections at E10.5 showed that Lmx1b HD expression is present in the wild-type (G) but lost in Lmx1bcko/− embryos (H). Arrowheads indicate Lmx1b HD expression in the wild type. I, J, Whole mount at E9.5 showed that Lmx1b HD is expressed in both the wild-type (I) and Lmx1a−/−; Lmx1bcko/− (J) embryos. K, L, Transverse sections through the fourth ventricle at E9.5 showed that Lmx1b HD expression is present in both the wild-type (K) and Lmx1a−/−; Lmx1bcko/− (L) embryos. Arrowheads indicate Lmx1b HD expression.