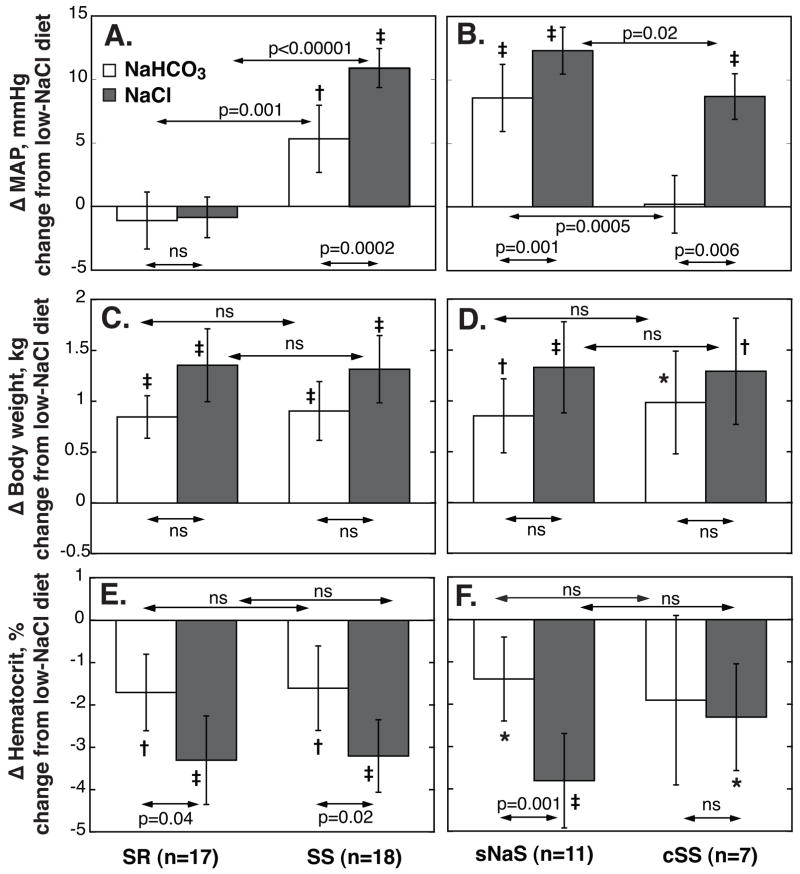
Figure 2. NaHCO3- (□) and NaCl-induced (
 ) changes in MAP, body weight (BW) and hematocrit in salt-resistant (SR) and salt-sensitive (SS) subjects, left panels, and in selective sodium-sensitive (sNaS) and classic salt-sensitive (cSS) subgroups, right panels.
) changes in MAP, body weight (BW) and hematocrit in salt-resistant (SR) and salt-sensitive (SS) subjects, left panels, and in selective sodium-sensitive (sNaS) and classic salt-sensitive (cSS) subgroups, right panels.
Values are average changes from baseline (average of days 5 and 6 of low-NaCl) on days 5 and 6 of Na+-loading periods. Values are means, error bars are 95% C.I. P values for within-group comparisons of Na+-loading vs low-NaCl period: ★P<0.05; †, P<0.01; and ‡ P<0.001; respectively. NaHCO3-loading induced a significant pressor response in SS but not in SR, panel A. In 11 of 18 SS the NaHCO3-induced pressor effects was ≥5 mmHg (sNaS), in 7 SS it was <5 mmHg (cSS), panel B. Responses of BW (panels C and D) and hematocrit (panels E and F) to Na+-loading did not differ between SR and SS and between sNaS and cSS, respectively.