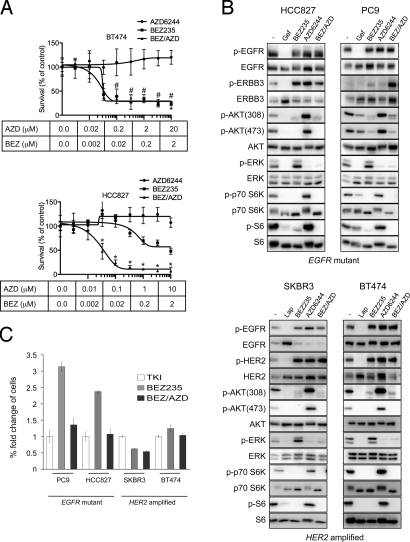
Fig. 1.
PI3K-mTOR inhibition effectively reduces cell viability in HER2-amplified breast cancers, but combined PI3K-mTOR and MEK inhibition is necessary to effectively reduce cell viability in EGFR mutant lung cancer cells. (A) HER2-amplified BT474 cells (top) and EGFR mutant HCC827 cells (lower) and were treated with increasing doses of the PI3K-mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235, the MEK inhibitor AZD6244, or the combination of both (BEZ/AZD), and total cell viability was determined after 72 h by staining cells with the nucleic acid stain, Syto60. Data are presented as the percent of viable cells versus DMSO (-) treated cells. ± S.D. Student's t-test were performed comparing BEZ with BEZ/AZD at indicated concentrations; * indicates a P value <0.001, # indicates P > 0.05 (not significant). (B) Cells were treated with either DMSO (-) or the indicated drug(s) for 6 h (TKIs 1 μM, NVP-BEZ235 0.2 μM for all cell lines, AZD6244 0.2 μM for SKBR3 cells, 1 μM for HCC827 and PC9 cells, and 2 μM for BT474 cells). Protein lysates were immunoblotted and probed with the indicated antibodies. (C) Cells were treated with the indicated drug(s) as in (B) for 16 days, and cell viability was determined by Syto60 assay. The fold difference of viable cells is presented relative to the viable cells treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor [TKI, gefitinib (gef) for HCC827 and PC9 cells, and lapatinib (lap) for SKBR3 and BT474 cells]. BEZ versus BEZ/AZD (HCC827, P < 0.001; PC9, P < 0.001), and BEZ versus TKI (HCC827, P < 0.001; PC9, P < 0.001).