Table 2.
Centrality measures used in this study
| Centrality | Formula | Description |
| In degree | Cu = kin(u) | Number of connections into node u |
| Out degree | Cu = kout(u) | Number of connections out from node u |
| Sphere degree | Cu = kout(u) + ∑w∩u kout(w); w is any neighbor of u. | Number of nodes at 1 or 2 connections from node u |
| Clustering coefficient | 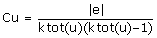 |
The fraction of connections between the neighbors of node u |
| 1/Clustering coefficient |  |
|
| Eccentricity | Cu = max{dist(u, w): w ∈ V} | The distance between node u and the most distant node in the net. |
| 1/Eccentricity | Cu = 1/max{dist(u, w): w ∈ V} | |
| Average distance | 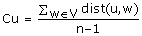 |
Average distance of node u to the rest of nodes in the net |
| Closeness | 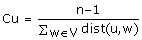 |
Inverse of average distance |
| Katz | 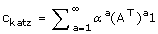 |
A node has a larger ckatz value while more paths reach it. |
| KatzR | 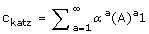 |
A node has a larger ckatz value while more paths leave the node. |
| PageRank | cPR = d P cPR + ((1 - d) 1) | The centrality of a node depends on its incoming connections and the relative connectivity of these connections |
| PageRankR | cPR = d PT cPR + ((1 - d) 1) | The centrality of a node depends on its outcoming connections and the relative connectivity of these connections |
| Integration | 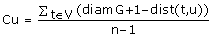 |
The easiness of reaching node u from any other node |
| Radiality | 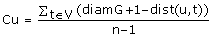 |
The easiness of reaching any node from node u |
| SP-betweenness | 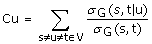 |
The fraction of shortest paths inside the network, which utilize node u |
In the table, kin(u), kout(u) and ktot(u) refer to the incoming, outgoing and total number of edges of node u. diamG refers to the diameter of the graph and dist(u, v) stands for the distance between nodes u and v. In clustering coefficient, |e| stands for the observed paths between the neighbours of a node. In Katz A is the adjacency matrix and α a damping factor. In PageRank d is a damping factor and P the transition matrix. In the formula for shortest path (SP) betweenness σG denotes the number of shortest path from s to t. For a more detailed description of these centralities, please read [17].
