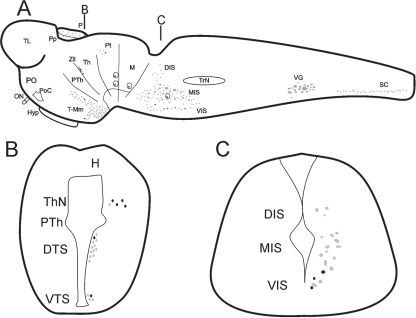
Fig. 1.
Schematic drawings of sagittal (A) and transverse (B and C) sections of the brain of a larval sea lamprey showing the distribution of double-labelled serotonin/GABA immunoreactive cells (black) in comparison with the distribution of serotonergic cells (grey). (A) Sagittal section of the larval brain/spinal cord (SC) showing the organization of the serotonergic nuclei and the location of the 5-HT-ir/GABA-ir cells within these nuclei. The black lines indicate approximately the positions of the transverse sections shown in (B) and (C). (B) Transverse section of the diencephalon showing the location of the 5-HT-ir/GABA-ir cells of the thalamic nucleus (ThN) and the dorsal and ventral tuberal subpopulation (DTS and VTS, respectively). (C) Transverse section of the rostral rhombencephalon showing the location of the 5-HT-ir/GABA-ir cells in the lamprey isthmus. Note the presence of double-labelled cells only in the ventral isthmic subpopulation (VIS) and the absence of this type of cell in the medial (MIS) and dorsal (DIS) subpopulations. H, habenula; Hyp, hypophysis; M, mesencephalon; ON, optic nerve; P, pineal organ; PO, preoptic region; PoC, postoptic commissure; Pp, parapineal organ, Pt, pretectum, PTh, prethalamus, Th, thalamus, TL, telencephalon, T-Mm, tuberal-mammillary nuclei, TrN, trigeminal nucleus; VG, vagal nucleus; Zli, zona limitans intrathalamica.