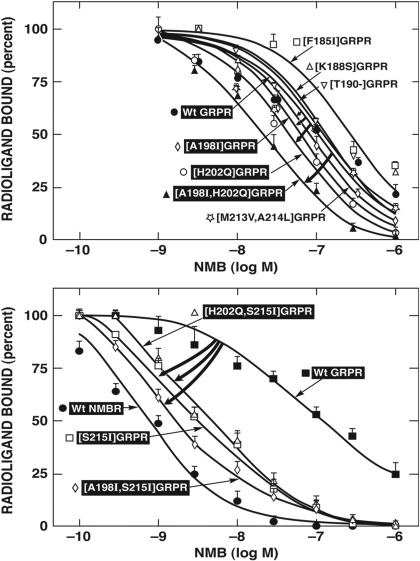
Fig. 5.
Affinities of NMB for wild-type GRPR and selected single and double amino acid(s) mutant GRP receptors (gain-of-affinity), with changes in the third EC region. These mutations were made by substituting, in GRPR, the different amino acids in the comparable positions of NMBR. The curved arrows indicate large gains in affinity of the mutant GRPR for NMB caused by the indicated mutation. All studies were performed in Balb-3T3 cells transiently transfected with the indicated wild-type or mutant receptor by using 50 pM 125I-[Tyr4]Bn as the ligand. Each point on the dose-inhibition curves is the mean ± S.E.M. from at least four separate experiments, and each point was determined in duplicate in each experiment. Data are expressed as the percentage of saturable binding when no unlabeled peptide was present