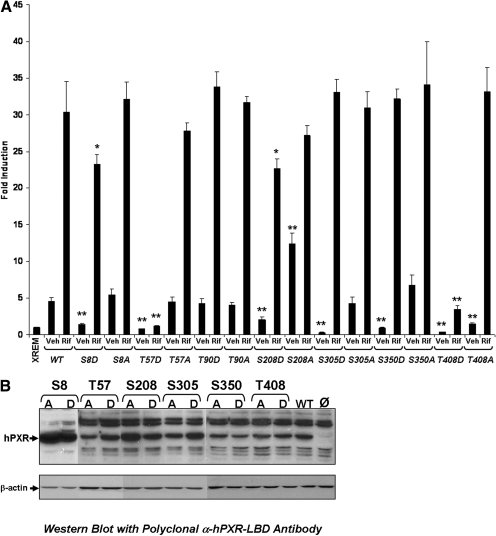
Fig. 2.
The basal transactivation capacity of mutant PXR proteins. A, CV-1 cells were transfected with the XREM-Luc reporter gene construct and expression vectors encoding wild-type or mutant PXR. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with either vehicle or 10 μM rifampicin. Luciferase activity was observed for an additional 24 h after drug treatment. PXR proteins containing phosphomimetic mutations at Thr57 and Thr408 were not activated by rifampicin treatment. The data are normalized to β-galactosidase activity and represented as fold induction ± S.D. (n = 4). Statistically significant differences compared with vehicle- and rifampicin-treated wild-type PXR values are denoted with an asterisk (∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗P, < 0.001). B, Western blot analysis using a polyclonal antibody that recognizes the entire LBD of human PXR was performed on extracts isolated from CV-1 cells that express wild-type or the indicated mutant PXR proteins.