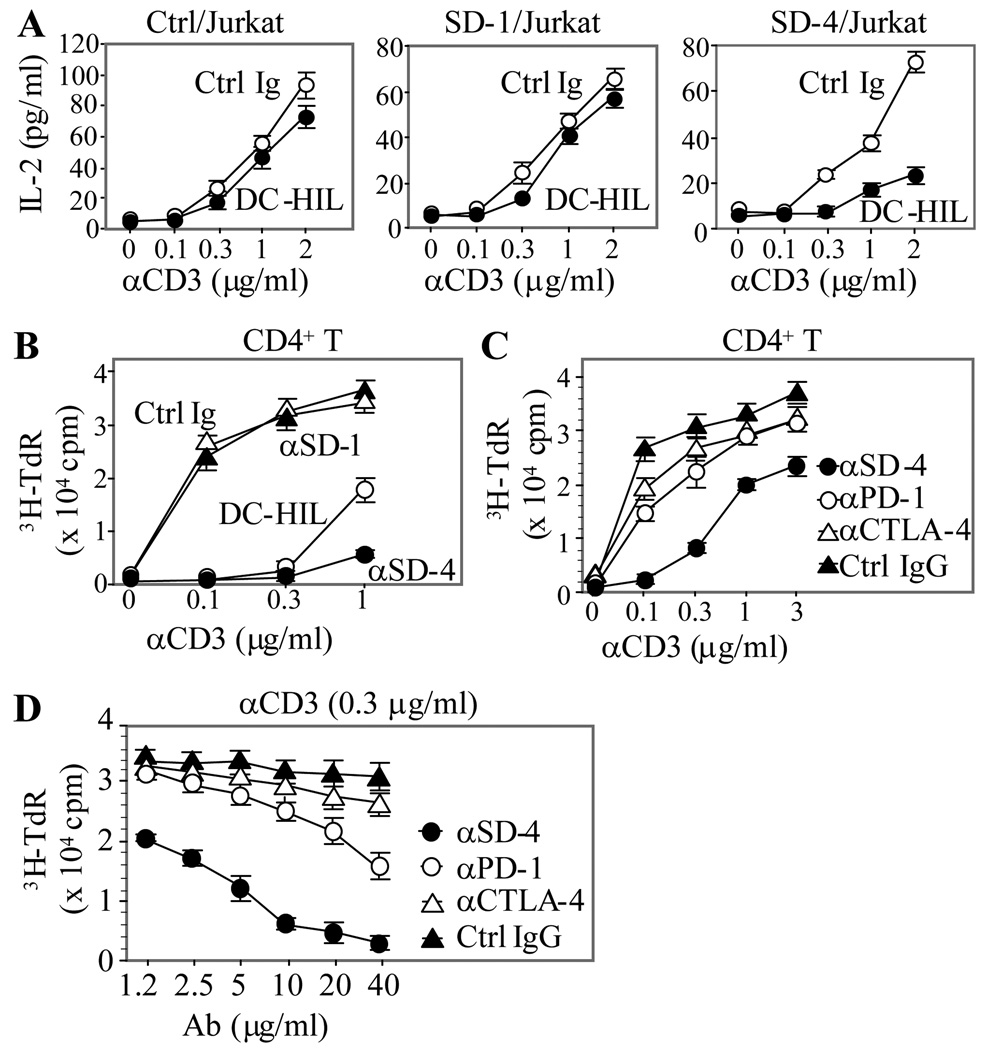
Figure 3. SD-4 acts as a negative regulator of anti-CD3 response.
(A) Three Jurkat transfectants were stimulated with immobilized anti-CD3 Ab (varying doses) and DC-HIL-Fc or control Ig (a constant dose of 10 ìg/ml) for 2 d. T cell activation was measured by IL-2 production (mean ± SD, n = 3). (B) Peripheral blood CD4+ T cells were cultured in 96-well plates precoated with anti-CD3 Ab at increasing doses and DC-HIL-Fc, anti-SD-1, anti-SD-4 Ab, or control Ig at each 10 µg/ml. (C and D) Inhibitory function of anti-SD-4 Ab (10 µg/ml) was compared with Ab directed against other inhibitory receptors (PD-1 and CTLA-4) by titrating with increasing doses of anti-CD3 Ab (C) or by titrating a constant dose of anti-CD3 Ab (0.3 µg/ml) with increasing anti-inhibitory receptor Ab (D). All treated T cells (B through D) were cultured for 3 d and activation assessed by 3H-thymidine incorporation (mean ± SD, n = 3). Effects of DC-HIL-Fc or anti-SD-4 Ab at all dose points were statistically significant (Student’s t test p<0.05), compared to control Ig or other Ab. All data shown are representative of at least 2 independent experiments.