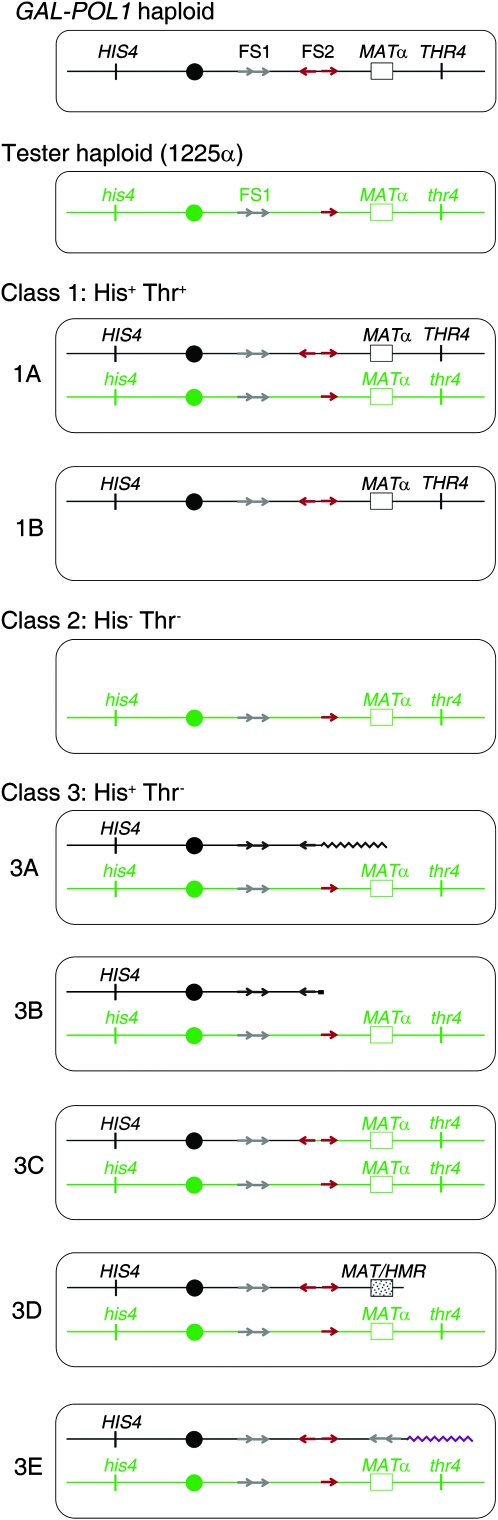
Figure 2.—
Classes of illegitimate diploids induced by low levels of DNA polymerase α. In our experiments, a GAL-POL1 MATα HIS4 THR4 haploid experimental strain was grown under conditions that result in low α-DNA polymerase. The strain was then mated to a tester strain (1225α) with the genotype MATα his4 thr4. Ty elements are shown as red (FS2) or gray (FS1) arrows, with the orientation of the arrow representing the orientation of the Ty element. On the basis of the phenotypes of the resulting diploids, they were classified as class 1 (His+ Thr+), class 2 (His− Thr−), or class 3 (His+ Thr−). Subsequent analysis showed that there were two types of class 1 events. Class 1A events were a consequence of fusions between two MATα strains without observed genomic changes; class 1B events were a consequence of loss of chromosome III from the tester strain. Class 2 events reflected loss of chromosome III from the experimental strain. The subclasses of class 3 were 3A (translocations with a breakpoint at FS1 or FS2 and at a Ty or δ-element on a nonhomologous chromosome), 3B (telomere-capped terminal deletion on the right arm of III), 3C (DSB on the right arm of III of the experimental strain, followed by repair from the homolog in the tester strain), 3D (deletion fusing MAT and HMR), and 3E (complex rearrangement with the FS2-centered palindrome described further in the text).