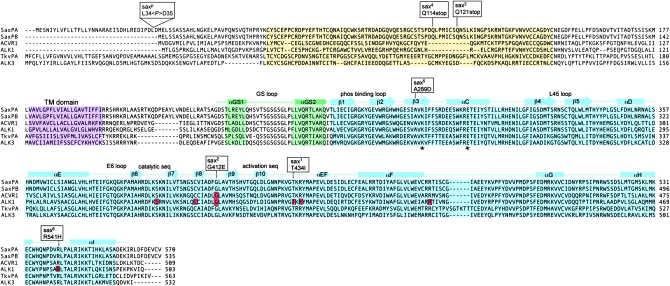
Figure 7.—
Sequence comparison of Sax (PA and PB isoforms), ACVR1 (ALK2), ALK1 (ACVRL1), Tkv (PA isoform), and ALK3. The extracellular ligand binding domain (yellow), the transmembrane domain (purple), the intracellular GS activation (green), and serine/threonine (blue) kinase domains are shaded. The structural elements of the cytoplasmic GS and kinase domains (based on the TβR1 structure) (Huse et al. 1999) are indicated above the sequence alignment. The positions of mutations associated with the sax alleles discussed are indicated above the sequence alignment. The positions of specific HHT2 and FOP mutations in ALK1 and ACVR1, respectively, are highlighted in red within the sequence. The asterisks mark the invariant Lys and Glu residues critical for stabilization of the catalytic segment with the N and C lobes of the kinase.