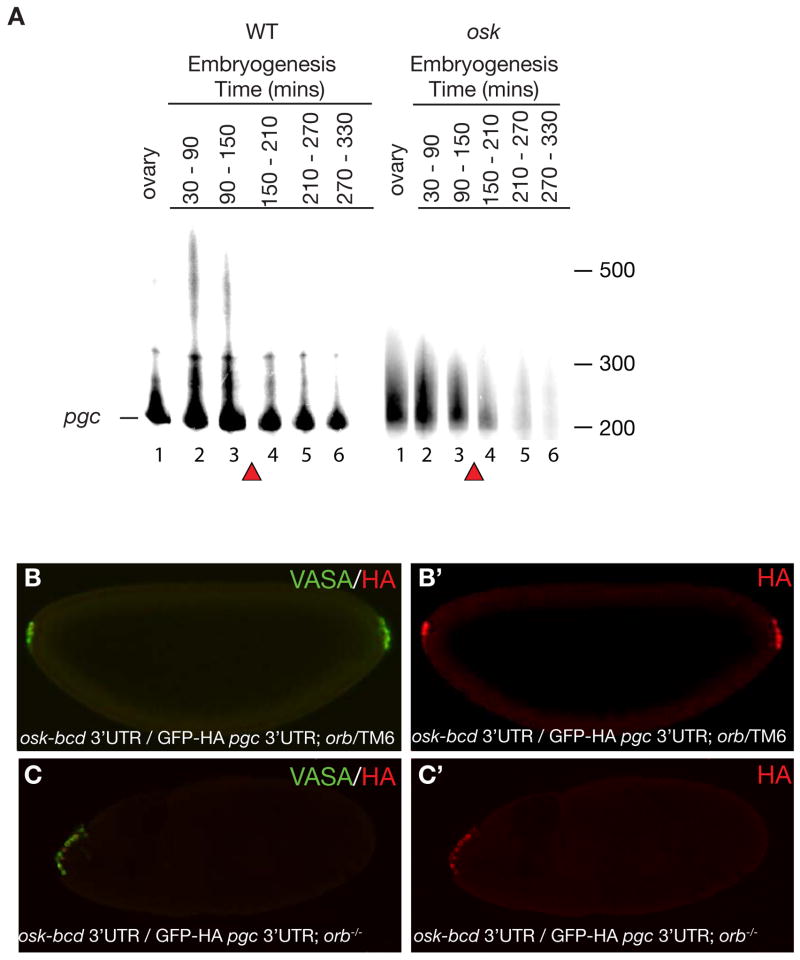
Figure 2. Translation of pgc is concurrent with poly(A) tail extension and is CPEB independent.
A. PAT assay was performed for pgc RNA as indicated in materials and methods and products were run on an urea denaturing acrylamide gel. Poly(A) tail length of ovaries and embryos from wild-type and osk mutant females. Lane 1: Ovary; Lane 2: 30–90 mins AEL (stage 1–3); Lane 3: 90–150 mins AEL (stage 3–4); Lane 4: 150–210 mins AEL (stage 4–5); Lane 5: 210–270 mins AEL (stage 5-6-7); Lane 6: 270–330 mins AEL (stage 8–10). The baseline band indicated by a line corresponds to the shortest amplified fragment at 200nt. Poly(A) tail length is measured form this line. Red triangles mark the maternal to zygotic transition during which unlocalized maternal RNAs are degraded. A loading control for wild-type and osk mutant embryos is shown in Supplementary Figure 9. B and B′. Germ cells are formed at both anterior as well as posterior poles of embryos from osk-bcd 3′UTR/ pnos::HA-GFP-HA-pgc 3′UTR; orbmel/TM6 mothers. (B) Merge of both VASA and HA antibody, (B′) stained for GFP-HA reporter. C and C′. Germ cell formation only at anterior pole and not posterior pole in embryos from osk-bcd 3′UTR/ pnos::HA-GFP-HA-pgc 3′UTR; orbmel /orb343 mothers. (C) Merge of both VASA and HA antibody, (C′) stained for GFP-HA reporter. Posterior of the embryo is to the right.