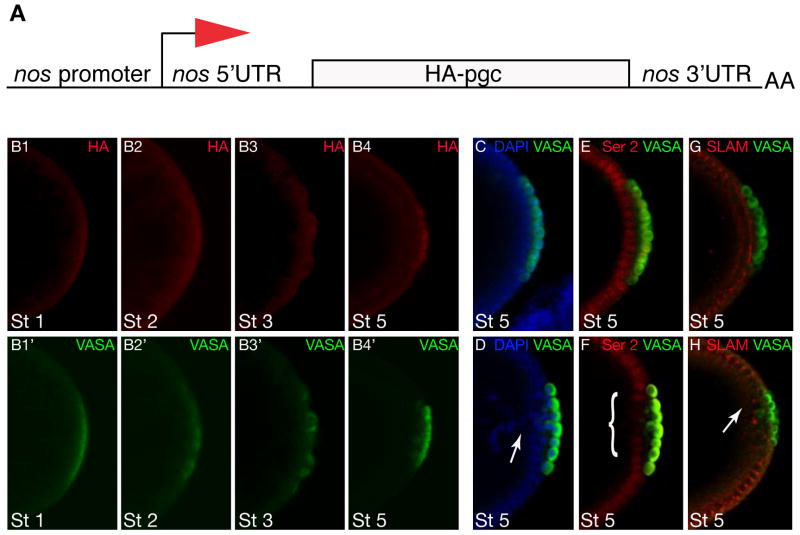
Figure 3. Precocious expression of PGC affects embryonic development.
A. Diagram showing the pnos::PGC-HA-nos 3′UTR construct used in this experiment to translate pgc in the germ plasm under the control of the nos 3′UTR. B. Nos-like translation pattern of embryos from mothers carrying pnos::PGC-HA-nos 3′UTR reporter construct. B1–B4 immuno-staining for HA shows translation in germ plasm and germ cells. B1′-B4′ immuno-staining for VASA shows staging of germ line development. C and D. Wild-type embryo (C) and embryo from pnos::PGC-HA-nos 3′UTR female (D) stained for nuclei in blue (DAPI) and germ cells in green (VASA). The somatic cells adjacent to the germ cells form a continuous epithelial layer in the wild type (C) but fail to cellularize properly and fall back into the yolk (“Pole hole phenotype”) in the embryo that precociously expresses PGC (arrow). E and F. Wild-type embryo (E) expresses high levels of active RNAPol II (detected by antibodies against the P-Ser2 epitope in the of RNAPol II CTD in red) in somatic cells adjacent to the germ cells (VASA, green); note that germ cells are transcriptionally silent due to PGC function. Embryo from pnos::PGC-HA-nos 3′UTR female (F) expresses reduced levels of the P-Ser2 epitope (red (marked by bracket)) in somatic cells adjacent to germ cells (VASA, green) because of expanded expression of PGC. G and H. Wild-type embryo (H) immunostained for Slow as molasses (SLAM) (red) a zygotically expressed gene required for somatic cellularization; germ cells stained for VASA in green. Expression of SLAM is disrupted in embryo from female carrying the pnos::PGC-HA-nos 3′UTR transgene (H, arrow). Stages as indicated, posterior is to the right.