Figure 3.
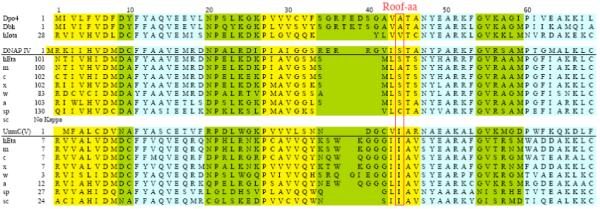
Amino acid alignment for the regions corresponding to aa1-69 in Dpo4 for eight Y-family DNAPs whose structure has been determined by X-ray crystallography (Dpo4, Dbh, scDNAP η, hDNAP ι and hDNAP κ) or by homology molecular modeling (hDNAPs η, E. coli DNAP IV and UmuC of DNAP V), along with additional sequences for DNAPs κ and η from several other species. Data are from references 47 and 48. α helices (blue), β sheets (yellow) and turns (green) are shown. Boxes indicate conserved amino acids (five of eight) or other notable amino acid similarities. Abbreviations: ss (Sulfolobus solfataricus) h, human (Homo sapien); m, mouse (Mus musculus); c, chicken (Gallus gallus); x, Xenopus laevis (frog); w, worm (Caenorhabditis elegans); a, Arabidopsis thaliana (plant); sc, Saccharomyces pombe (fission yeast); sp, Saccharomyces cerevisae (budding yeast). Colors: blue, α-helicies; yellow, β-strands; green, loops.
