Figure 1.
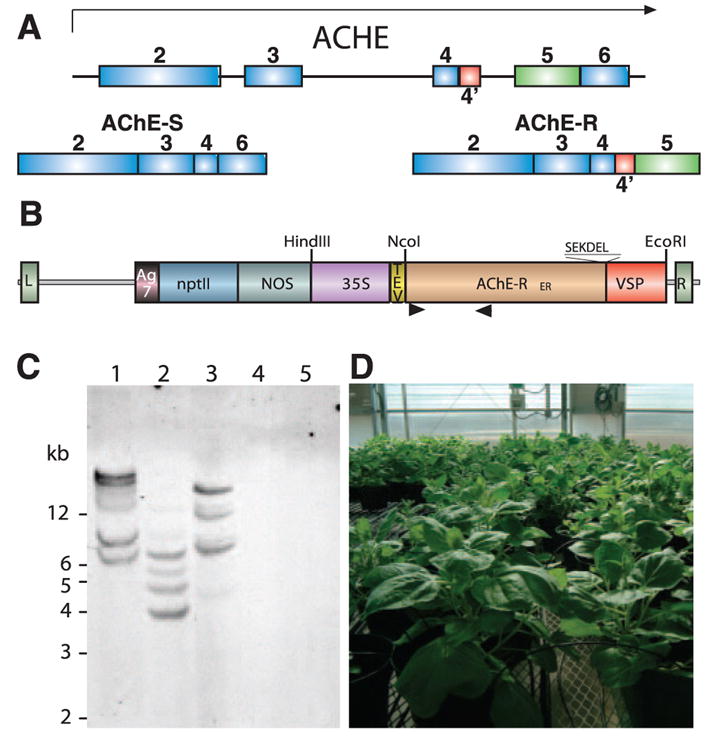
Expression of AChE-RER in plants. A) AChE-S and AChE-R are alternative splicing variants with distinct C termini. B) The AChE-RER expression vector. L, left border; R, right border; Ag7, the nopaline synthase polyadenylation signal; nptII, the kanamycin resistance marker; NOS, the nopaline synthase promoter; 35S, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; TEV, the translation enhancer region of the tobacco etch virus; AChE-RER, codon-optimized coding region for human AChE-R containing the C-terminal SEKDEL endoplasmic reticulum retention signal; VSP, the 3′ UTR of the soybean vegetative storage protein; arrowheads, locations of primers used to generate probe for DNA blot analysis. C) DNA blot analysis. Genomic DNA was extracted from the highest expressing N. benthamiana line (2D) (lanes 1–3) and WT plants (lanes 4, 5) and digested with EcoRI (lanes 1, 4), NcoI (lanes 2, 5), and HindIII (lane 3). D) Large-scale cultivation of 2D N. benthamiana in controlled growth facility at Arizona State University.
