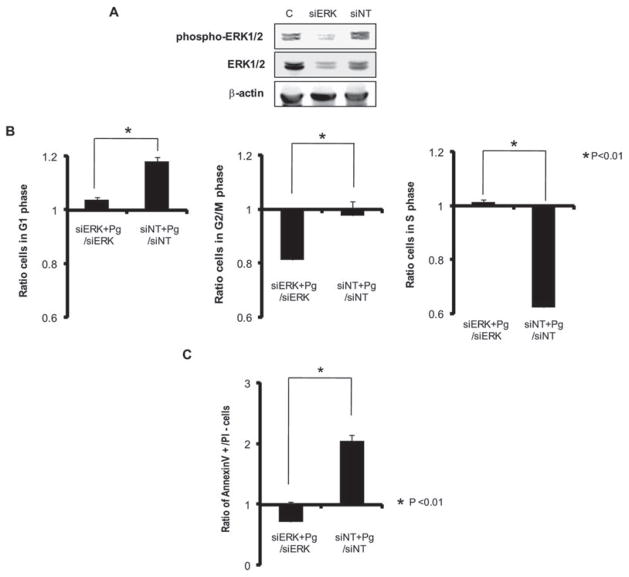
Fig. 9. Knock-down of ERK1/2 by siRNA represses P. gingivalis-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. HTR-8 cells were transfected with siRNA to ERK1/2 or with a no-target control (siNT).
A. Transfected (72 h) or control (c) cells probed with antibodies to ERK1/2 or to phospho-ERK1/2.
B. Transfected (72 h) HTR-8 cells were infected with P. gingivalis at an moi of 200 for 48 h, and cell cycle distribution was determined by flow cytometry. The fold change in numbers of cells in each phase of the cell cycle was calculated in cells transfected with siRNA to ERK1/2 or siNT and infected with P. gingivalis, and compared to transfected, uninfected cells. Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments and analysed with a t-test.
C. Transfected (72 h) HTR-8 cells were infected with P. gingivalis at an moi of 200 for 48 h, stained with Annexin V/PI and analysed by flow cytometry. The fold change in the number of Annexin V+/PI− cells was calculated in cells transfected with siRNA to ERK1/2 or siNT and infected with P. gingivalis, and compared to transfected, non-infected cells. Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments and analysed with a t-test.