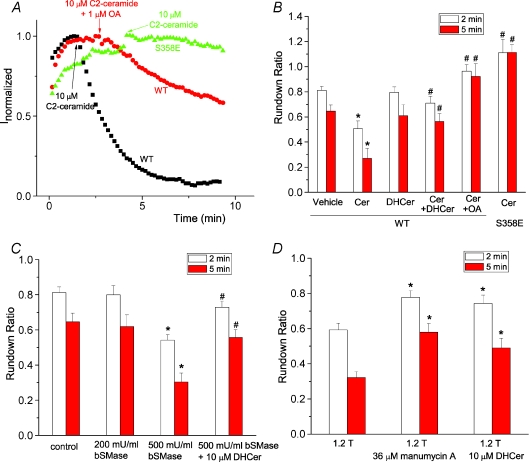
Figure 6. Ceramide mediates hypertonic inhibition of hBest1 currents.
A, effects of ceramide on wild-type hBest1 currents recorded from control cells (squares), cells pretreated with 1 μm okadaic acid (circles), and cells transfected with S358E mutant (triangles). C2-ceramide at 10 μm was applied when currents reached peak as indicated by the arrow. B, ceramide inhibited hBest1 currents through dephosphorylation of S358. C2-ceramide (Cer) at 10 μm, 10 μm dihydroceramide (DHCer), 10 μm C2-ceramide plus 10 μm dihydroceramide together (Cer+DHCer), 10 μm C2-ceramide and 1 μm OA together, or vehicle control (0.2% dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO)) was applied when currents reached peak amplitudes as in A. The channel rundown was measured as ratio of amplitudes of the current 2 min (open columns) or 5 min (filled columns) after drugs were applied at the peak to the amplitudes at the peak (n= 5–9 cells; *P < 0.05 versus vehicle control; #P < 0.05 versus wild-type currents treated with ceramide only). C, effects of bacterial sphingomyelinase (bSMase) on wild-type hBest1 channel rundown. bSMase at 200 mU ml−1, 500 mU ml−1 bSMase, and 500 mU ml−1 bSMase and 10 μm dihydroceramide together were applied when currents reached peak amplitudes as described in A. The channel rundown was measured as described in B (n= 6–9 cells. *P < 0.05 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus 500 mU ml−1 bSMase only). D, blockade of hypertonic inhibition of hBest1 currents by manumycin A and dihydroceramide. Cells were pretreated with 36 μm manumycin for 0.5–1 h, or with 10 μm dihydroceramide for 5–10 min. Hypertonic solutions containing 36 μm manumycin or 10 μm dihydroceramide were applied when currents reached peak amplitudes as described in A. The channel rundown was measured as described in B. n= 6–10. *P < 0.05 versus control.