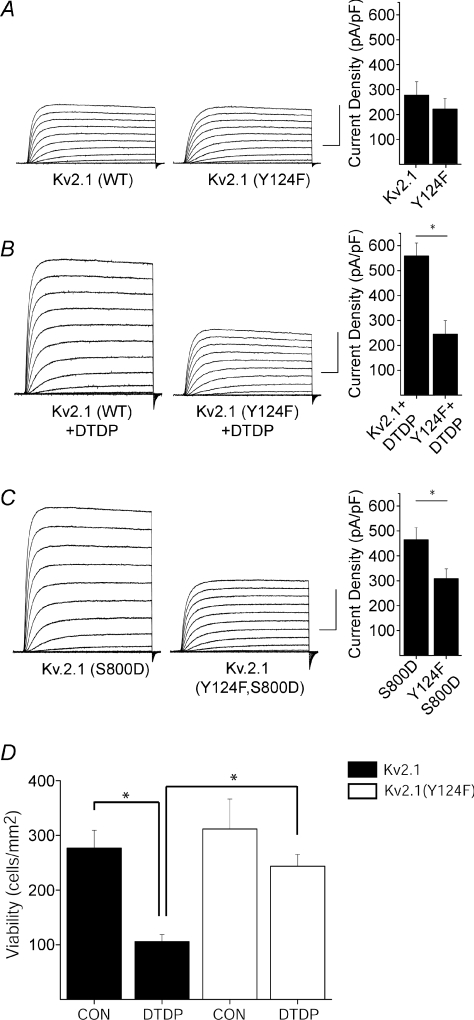
Figure 1. Y124 is essential for the apoptotic K+ current surge.
A (left), representative whole-cell K+ currents from wild-type Kv2.1- and Kv2.1(Y124F)-expressing CHO cells. Currents were obtained 24 h post-transfection and evoked by sequential 10 mV voltage steps to +80 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Calibration: 5 nA, 25 ms. Right, mean ±s.e.m. current densities from wild-type Kv2.1-expressing (n= 15) and Kv2.1(Y124F)-expressing CHO cells (n= 10). B (left), representative whole-cell K+ currents from wild-type Kv2.1- and Kv2.1(Y124F)-expressing CHO cells treated with DTDP. Calibration: 5 nA, 25 ms. Right, mean ±s.e.m. current densities from wild-type Kv2.1- (n= 12) and Kv2.1(Y124F)-expressing (n= 9) CHO cells (*P < 0.05; 2-tailed t test). C (left), representative currents from Kv2.1(S800D)- and Kv2.1(Y124F, S800D)-expressing CHO cells. Calibration: 5 nA, 25 ms. Right, mean ±s.e.m. current densities from Kv2.1(S800D)-expressing (n= 11) and Kv2.1(Y124F,S800D)-expressing (n= 13) CHO cells (*P < 0.05; 2-tailed t test). D, Y124F mutation disrupts Kv2.1-mediated apoptosis. CHO cells were cotransfected with eGFP plus empty vector and either Kv2.1 or Kv2.1(Y124F) and 24 h later exposed to 30 μm DTDP (15 min). Viability was assayed 24 h post-treatment by counting GFP-positive cells. Values represent the mean ±s.e.m. (n= 3) and are representative of 3 separate, independent experiments (*P < 0.05; ANOVA/Bonferroni).