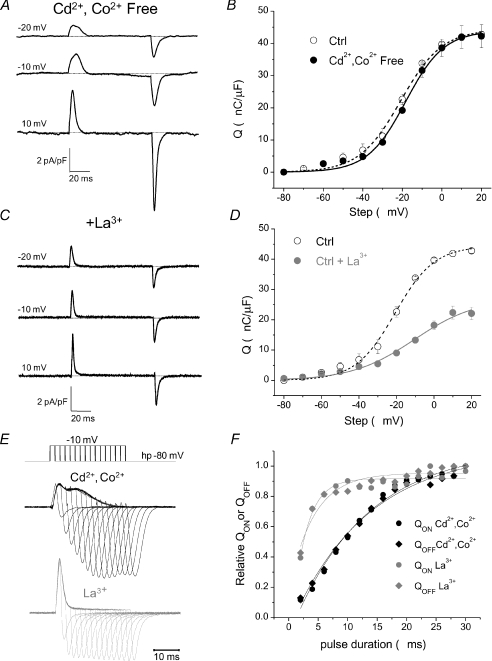
Figure 10. La3+ profoundly modifies intra-membrane charge movement.
A, charge movement currents recorded using an external solution lacking Cd2+ and Co2+ exhibit a temporally delayed component and similar current kinetics to fibres bathed in our standard control solution. Ca2+ was reduced to 0.5 mm and 10 mm Mg2+ was added to the external solution to block inward ionic components. B, fibres bathed in control external solution (open circles, dashed line) demonstrate a very similar Q vs. V relationship to fibres bathed in Cd2+ and Co2+ free external solution (filled circles, continuous line). C, charge movement currents recorded using an external solution supplemented with 0.3 mm La3+ exhibit rapid current kinetics and no clear temporally delayed ‘hump’ component. D, fibres bathed in our control external solution supplemented with La3+ demonstrate decreased maximal charge moved and a rightward shift in the voltage dependence of charge movement when compared to fibres bathed in our standard external solution. E, charge movement currents recorded in control and La3+-treated fibres in response to depolarizing pulses to −10 mV of increasing duration (2 ms increments) to evaluate charge movement conservation. F, QON or QOFFvs. pulse duration for the complete set of pulses of corresponding traces illustrated in E. The normalized charge–pulse duration relationships for both QON and QOFF are fitted to single exponential functions (continuous lines). The calculated time constant for charge development in the Cd2+/Co2+ exposed fibre was 13 ms, compared to 2.4 ms for the fibre exposed to La3+.