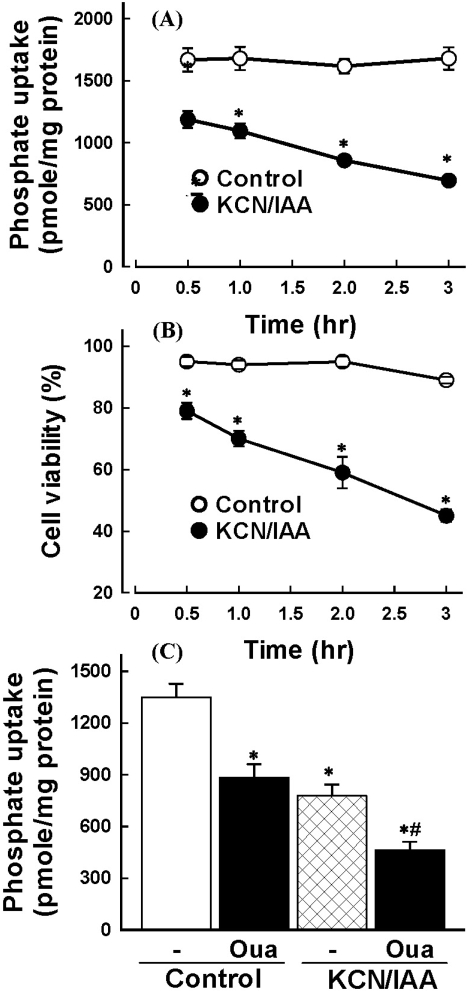
Fig. 1.
Effect of ATP depletion on Na+-dependent phosphate uptake (A) and cell viability (B) in primary cultured renal proximal tubular cells. Cells were exposed to medium with 2.5 mM potassium cyanide/0.1 mM iodoacetic acid (KCN/IAA) or without (Control) for 0~3 hr at 37℃. Na+-dependent phosphate uptake and cell viability were measured as described in 'Materials and Methods'. Data are mean±SEM of four independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05 compared with control. (C) Effect of ATP depletion on Na+-dependent phosphate uptake in primary cultured renal proximal tubular cells which were treated with ouabain. Cells were exposed to medium with 2.5 mM potassium cyanide/0.1 mM iodoacetic acid (KCN/IAA) or without (Control) in the presence or absence of 2 mM ouabain for 120 min at 37℃. Na+-dependent phosphate uptake was measured as described in 'Materials and Methods'. Data are mean±SEM of four independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05 compared with control; #p<0.05 compared with ouabain alone.