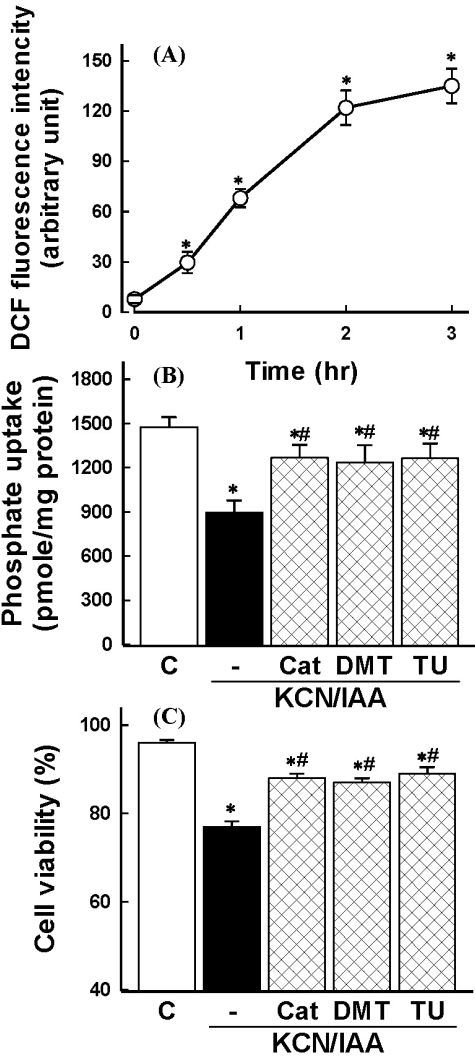
Fig. 2.
(A) Time course of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in primary cultured renal proximal tubular cells during exposure to ATP depletion. Cells were exposed to 2.5 mM potassium cyanide/0.1 mM iodoacetic acid (KCN/IAA) for various times and ROS generation was measured. Shown is the net increase of DCF fluorescence (arbitrary units) calculated by subtracting the values for the control cells from the corresponding values for KCN/IAA-treated cells. Data are mean±SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05 compared with zero (0) time. (B-C) Effect of radical scavengers on inhibition of phosphate uptake (B) and cell death (C) induced by ATP depletion. Cells were exposed to KCN/IAA in the presence or absence of 500 units/ml catalase (Cat), 30 mM dimethylthiourea (DMTU), or 30 mM thiourea (TU) for 3 hr at 37℃. Na+-dependent phosphate uptake and cell viability were measured as described in 'Materials and Methods'. Data are mean±SEM of four independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05 compared with control; #p<0.05 compared with KCN/IAA alone.