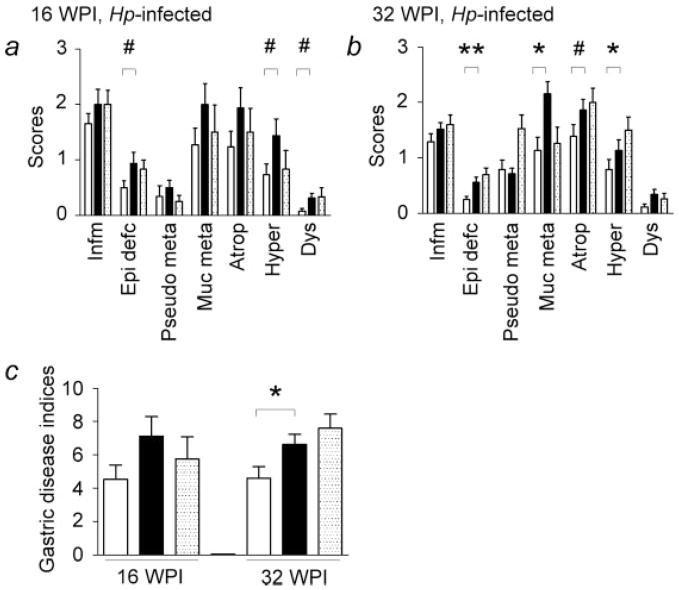
Figure 3.
Histological scores and gastric disease indices in H. pylori (Hp)-infected mice. Gulo−/− mice supplemented with high vitamin C had similar gastric lesions and gastric disease indices compared to C57BL/6 (WT) (dotted bars) mice at 16 and 32 WPI. (a) At 16 WPI, there was a trend for gulo−/− mice supplemented with low vitamin C (white bars) compared to those supplemented with high vitamin C (black bars) for less severe epithelial defects, foveolar hyperplasia, and dysplasia (#, 0.05 < p < 0.10). (b) At 32 WPI, H. pylori-infected gulo−/− mice supplemented with low vitamin C had significantly lower degrees of epithelial defects, mucous metaplasia, and foveolar hyperplasia relative to those supplemented with high vitamin C (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). There was a trend toward less severe oxyntic atrophy in gulo−/− mice supplemented with low vitamin C compared to those mice supplemented with high vitamin C (#, 0.05 < p < 0.10). (c) At 32 WPI, gastric disease indices were significantly lower in gulo−/− mice that received low vitamin C than those mice receiving high vitamin C (*, p < 0.05). Infm, inflammation; Epi defc, epithelial defects; Pseudo meta, psuedopyloric metaplasia; Muc Meta, mucous metaplasia; Atroph, oxyntic atrophy; Hyper, foveolar hyperplasia; Dys, dysplasia.