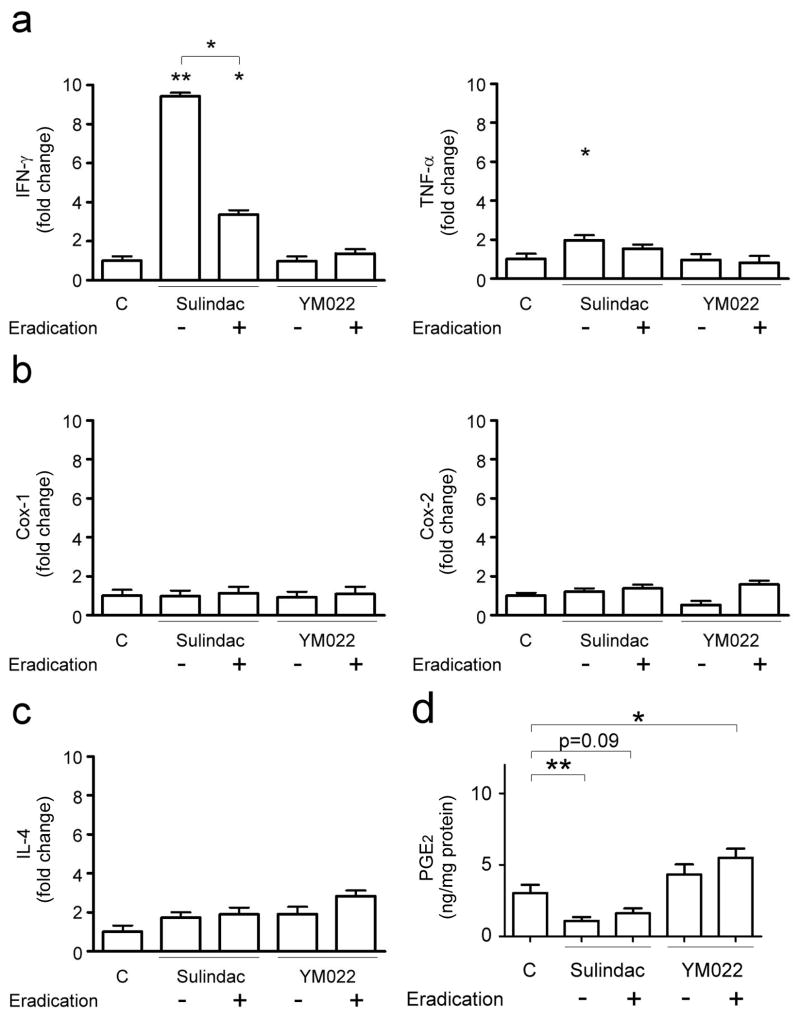
Figure 4.
mRNA expression levels of Th1 cytokines Ifn-γ and Tnf-α (a), Cox-1 and Cox-2 (b), Th2 cytokine Il-4 (c), and gastric PGE2 levels in H. pylori-uninfected mice. Data are presented as fold change relative to untreated, uninfected mice. Sulindac significantly up-regulated gastric Ifn-γ and Tnf-α (a) mRNA levels (p<0.01 and <0.05, respectively). Ifn-γ mRNA levels in mice receiving sulindac and antimicrobial (eradication) were lower than those in mice receiving sulindac (p<0.05), but were higher than untreated mice (p<0.05). Tnf-α mRNA levels in mice receiving sulindac and antimicrobial therapy were comparable to untreated mice or mice receiving sulindac. In contrast, YM022 or the combination of YM022 and antimicrobial therapy had no effect on gastric expression of Ifn-γ and Tnf-α. Gastric expression of Cox-1, Cox-2 (b), or Il-4 (c) was not influenced by sulindac or YM022 alone or in combination with antimicrobial therapy. Gastric PGE2 levels (d) were lower in mice receiving sulindac alone (p<0.01) and a combination of sulindac and antimicrobial therapy (p=0.09), but higher in mice receiving a combination of YM022 and antimicrobial therapy (p<0.05). (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 when compared to untreated, uninfected mice or comparison as indicated).