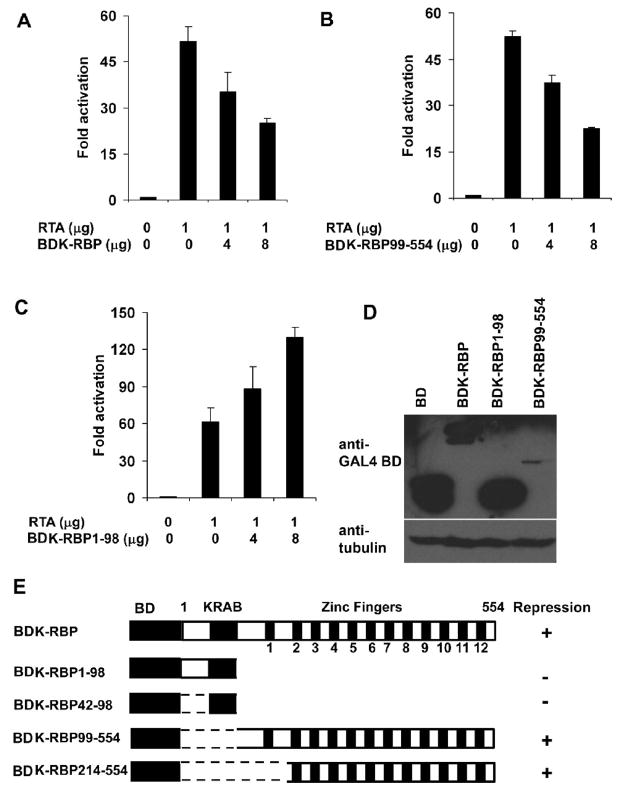
FIG. 6.
Effect of RTA-mediated transactivation of ORF57 promoter (p57Pluc1) by K-RBP and its mutants in BJAB cells. (A–C) BJAB cells were transfected with 1 μg of p57Pluc1, expression plasmids of RTA and GAL4BD-tagged K-RBP in (A), K-RBP99-554 (zinc fingers) in (B), K-RBP1-98 (KRAB) in (C). The luciferase activities were detected at 48 h post-transfection. In all transfections, the total DNA amounts used in each transfection were normalized by the addition of control expression plasmid. The basic promoter activity was normalized as 1 fold. The error bars indicate standard deviations of at least 3 independent experiments. Transfection efficiency for each experiment was normalized using a β-Gal expression plasmid as internal control. (D) The expression of K-RBP and its mutants. The indicated proteins expressed from plasmids were immunoblotted with rabbit anti-GAL4BD antibody. The higher molecular band from the control plasmid in the first lane is probably a GAL4BD fusion protein translated from a read-through transcript from the vector. Tubulin was used as the loading control. (E) Schematic diagrams of K-RBP deletion mutants used and their effects on RTA-mediated ORF57 transactivation. “+” and “−” indicate the ability of the various deletion clones to repress RTA-mediated transactivation.