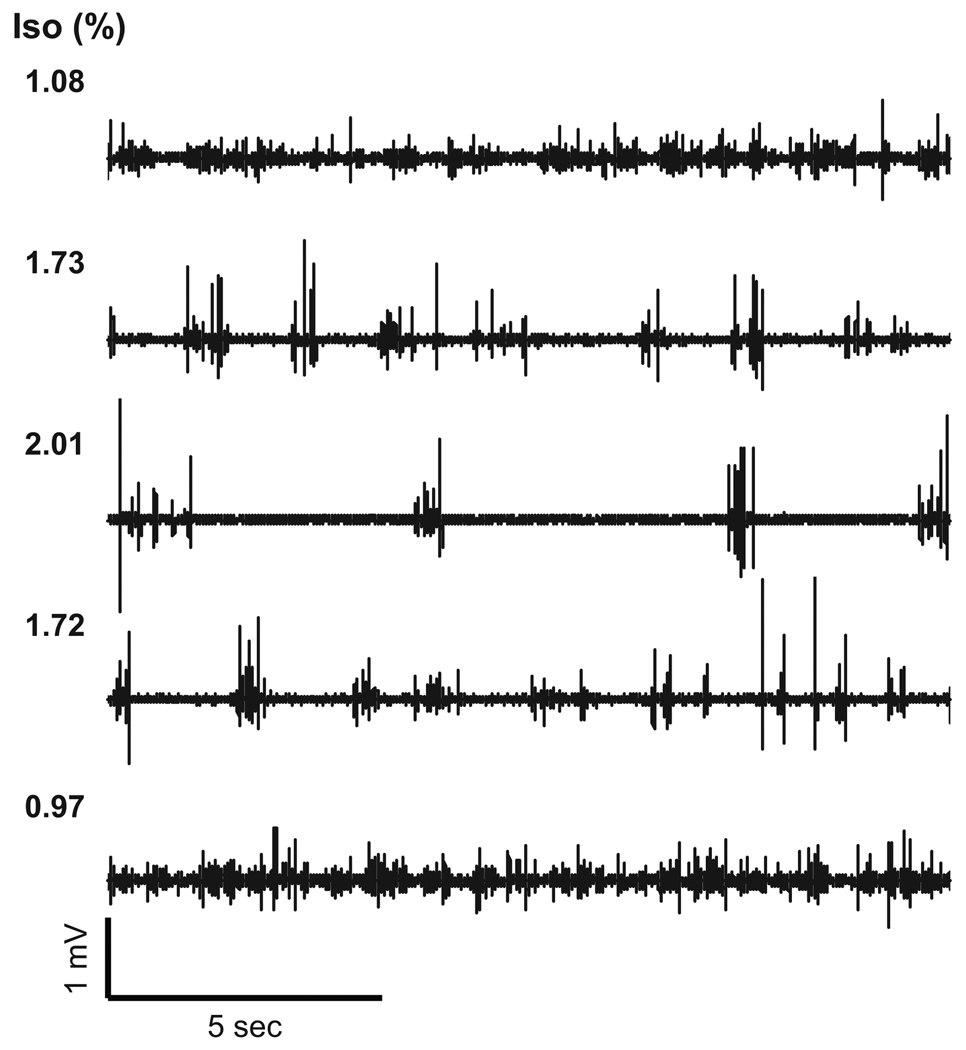
Figure 1. Baseline spontaneous field potentials induced by variable doses of isoflurane.
In this representative animal, the isoflurane concentration (Iso) was changed from 1.1% (top) to 2.0% (middle) and again adjusted to 1.0% (bottom). In each condition, the spontaneous FP activity varied depending on the isoflurane dose, and a consistent pattern was reproducibly observed in the respective doses. At high-dose conditions (≥ 1.7%), a burst-suppression pattern was evident. This pattern was consistently observed across all animals.