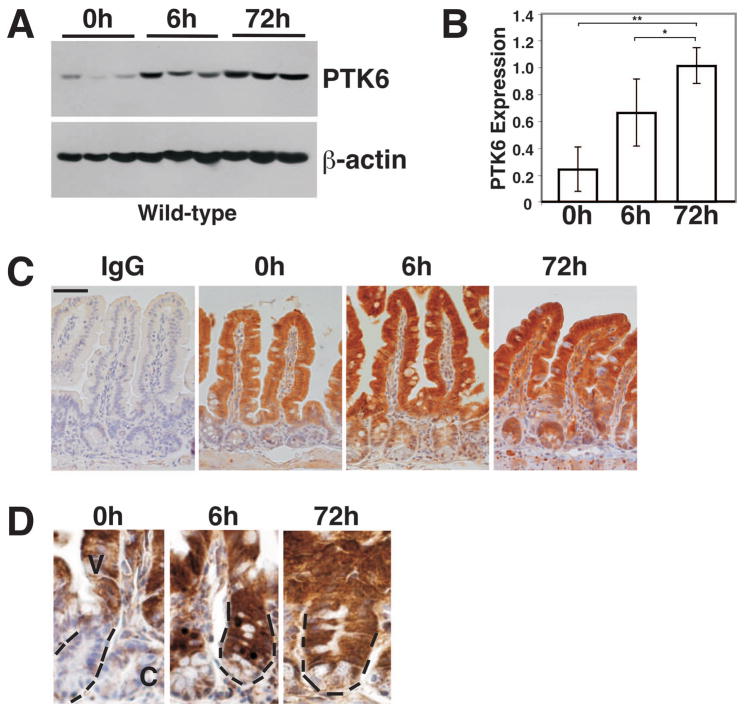
Figure 1. PTK6 protein expression is induced by γ-irradiation.
(A) Immunoblotting of untreated (0 h) and γ-irradiated (8 Gy) wild-type mouse lysates (6 h and 72 h following irradiation) from small intestine with antibodies against PTK6 and β-actin as a loading control. Results obtained using lysates from three different animals per timepoint are shown. (B) Quantitation of PTK6 protein expression. PTK6 protein levels were normalized to β-actin expression. The bars represent the mean ± S.D. A significant increase in PTK6 protein expression is detected in irradiated mice (*P-value = 0.028; **P-value = 0.040). (C) PTK6 is induced in the crypt epithelial cells after irradiation. Immunohistochemistry was performed to examine PTK6 expression in untreated and irradiated wild-type animals. Immunostaining for IgG served as a control. While PTK6 protein expression is restricted to the villus epithelium of untreated mice, it is also detected in the crypt of irradiated mice. Size bar represents 50 μm. (D) Higher magnification showing immunolocalization of PTK6 in crypt cells. At 6 and 72 h PTK6 positive cells are evident throughout most of the crypt, with weakest expression in Paneth cells localized at the base. PTK6 immunoreactivity was detected with DAB (brown stain). Dashed lines mark a crypt (C) in each panel at the same magnification.