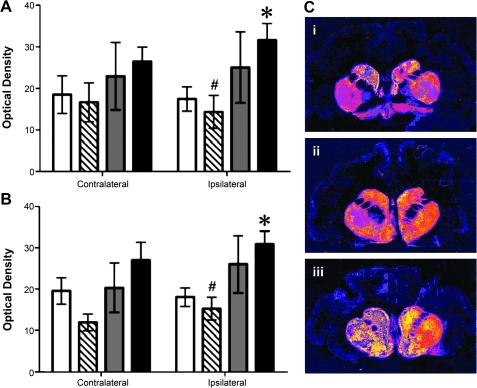
FIG. 5.
Tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in the putamen after infusion of AAV2-GDNF to the putamen. Open columns, control animals that received a PBS infusion; hatched columns, low-dose putamen group; gray columns, substantia nigra group; solid columns, high-dose putamen group. Columns and error bars represent mean (±SEM) optical density measurements (relative to white matter). (A) Putamen: Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between hemisphere and treatment (p < 0.05); unpaired post-hoc test for right side: PBS versus high-dose putamen, p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05. Post-hoc analyses by unpaired t tests indicated a significant difference between PBS and high-dose putamen treatment groups (*p < 0.05). In addition, mean optical density in the low-dose putamen group was significantly less than that measured in the high-dose putamen group (#p < 0.05). (B) Caudate nucleus: Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of side (p = 0.02); one-way ANOVA (p < 0.01). Unpaired t tests (one-tailed): PBS versus HD putamen treatment (*p < 0.05), LD putamen versus HD putamen (#p < 0.01). (C) False color TH staining of representative sections from (i) LD putamen, (ii) SN, and (iii) HD putamen.