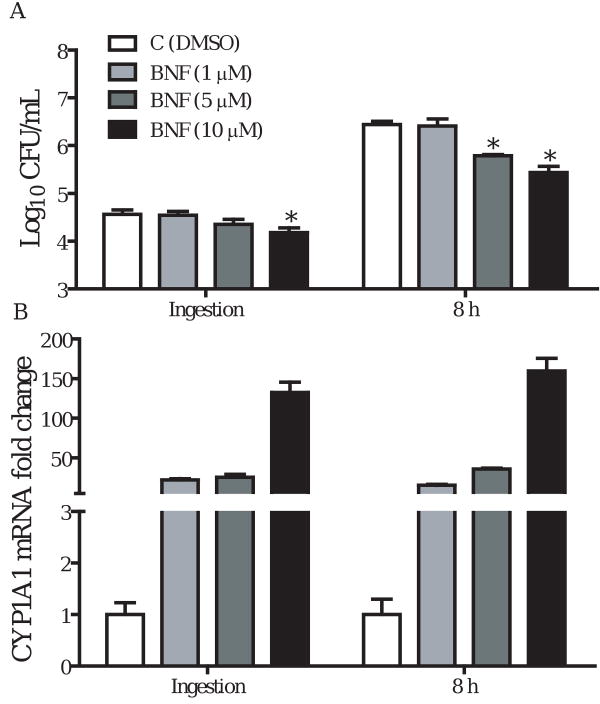
Figure 2.
BNF dose-dependently inhibits the invasion and intracellular growth of L. monocytogenes in TIB73 cells. TIB73 cells were treated with 1 ( ), 5 (
), 5 ( ), or 10 μM (
), or 10 μM ( ) of BNF for 5 h prior to infection with 105 log-phase L. monocytogenes for 2 h (Ingestion). Cells were then washed extensively to remove extracellular Listeriae and incubated in media with 5 μg/mL gentamycin for an additional 8 h. DMSO was included as a vehicle control (
) of BNF for 5 h prior to infection with 105 log-phase L. monocytogenes for 2 h (Ingestion). Cells were then washed extensively to remove extracellular Listeriae and incubated in media with 5 μg/mL gentamycin for an additional 8 h. DMSO was included as a vehicle control ( ). A. Infected cells were lysed in sterile water to quantify the number of viable L. monocytogenes. Data represent the mean±SEM Log10CFU/mL of four independent experiments that were performed. *: p<0.05 in comparison to the vehicle control. B. Parallel sets of TIB73 cells were used to isolate total RNA for real-time RT-PCR analyses of CYP1A1. CYP1A1 mRNA expression was presented as the mean±SEM fold change, relative to control samples, after normalization to that of GAPDH in the same samples.
). A. Infected cells were lysed in sterile water to quantify the number of viable L. monocytogenes. Data represent the mean±SEM Log10CFU/mL of four independent experiments that were performed. *: p<0.05 in comparison to the vehicle control. B. Parallel sets of TIB73 cells were used to isolate total RNA for real-time RT-PCR analyses of CYP1A1. CYP1A1 mRNA expression was presented as the mean±SEM fold change, relative to control samples, after normalization to that of GAPDH in the same samples.