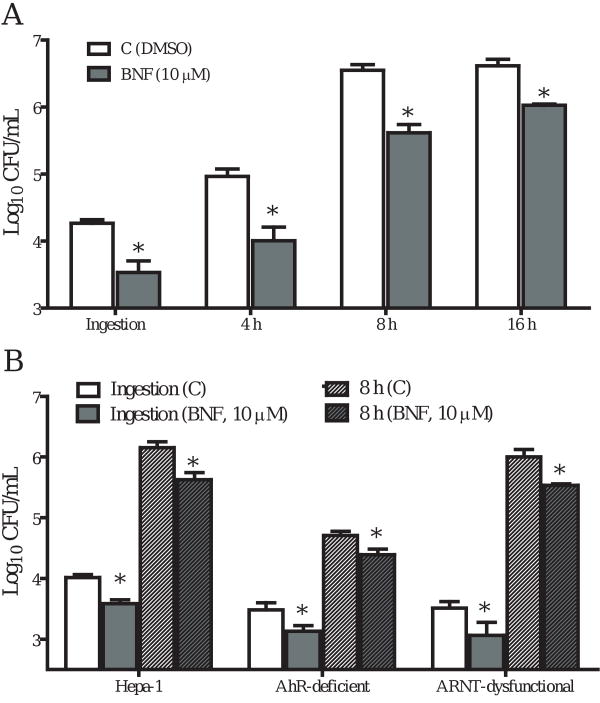
Figure 5.
BNF inhibits the ingestion and intracellular multiplication of L. monocytogenes in AhR-deficient and ARNT-dysfunctional Hepa cells. Hepa-1 (wild type) and AhR-deficient and ARNT-dysfunctional Hepa cells were treated with DMSO or BNF (10 μM) for 5 h before being infected with 105 log-phase L. monocytogenes for 2 h (Ingestion). Cells were then washed extensively to remove extracellular Listeriae and incubated in media with 5 μg/mL gentamycin for 8 h. Cells were then lysed in sterile H2O to determine the CFU of L. monocytogenes. Data illustrate the mean±SEM Log10CFU/mL of three separate experiments that were performed. *: p<0.05, as compared to the corresponding controls. A. BNF ( ) inhibited the ingestion and intracellular growth of L. monocytogenes in the WT Hepa-1 cells at all the times tested as compared to the DMSO control (
) inhibited the ingestion and intracellular growth of L. monocytogenes in the WT Hepa-1 cells at all the times tested as compared to the DMSO control ( ). B. The inhibitory effects of BNF on L. monocytogenes persist as seen in AhR-deficient and ARNT-dysfunctional Hepa cells. Used symbols indicate:
). B. The inhibitory effects of BNF on L. monocytogenes persist as seen in AhR-deficient and ARNT-dysfunctional Hepa cells. Used symbols indicate:  : Ingestion, DMSO control;
: Ingestion, DMSO control;  : Ingestion, BNF (10 μM);
: Ingestion, BNF (10 μM);  : 8 h, DMSO control;
: 8 h, DMSO control;  : 8 h, BNF (10 μM).
: 8 h, BNF (10 μM).