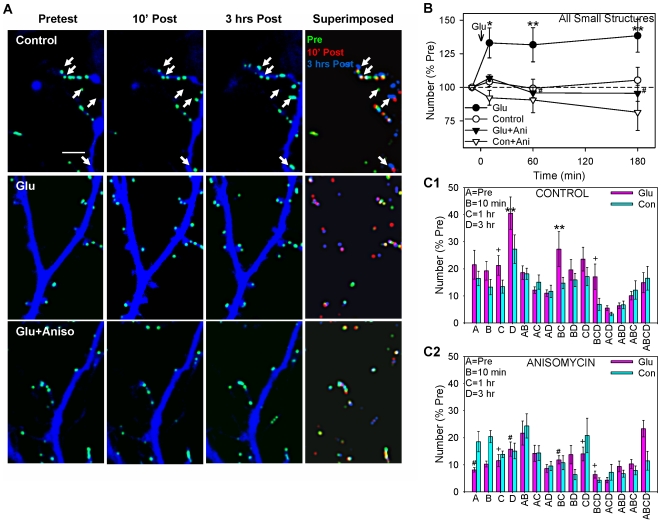
Figure 8. Glutamate produces a protein synthesis-dependent long-lasting increase in the number of small structures, which is due to a prolonged increase in the assembly of new structures.
A. Examples of small structures (light blue) before (Pretest), 10 min and 3 hrs after (Post) brief application of saline (control), glutamate, or glutamate following pretreatment with anisomycin. In the last column images from the 3 times in each experiment have been superimposed and color coded so that structures that were present at different combinations of times are represented by different combinations of colors (pretest only green, 10 min only red, 3 hrs only blue, pretest and 10 min yellow, pretest and 3 hrs light blue, 10 min and 3 hrs purple, and all three times white). Scale bar, 10 µm. B. Average time course of changes in the total number of small structures (n = 14 control dishes, 14 glutamate, 6 anisomycin, 6 glutamate + anisomycin). There were significant overall effects of glutamate (F[1,36] = 4.12, p<0.05) and anisomycin (F = 5.55, p<0.05) in a 3-way ANOVA with one repeated measure (time). The number of structures in one field (94×142 µm) per dish has been normalized to the number before glutamate application (pretest) in each experiment. The average pretest value per field was 119, not significantly different between the groups by a 1-way ANOVA. C. Average number of structures with different life histories: present only in the pretest (A), 10 min (B), 1 hr (C), 3 hrs (D), and various combinations of times (AB, AC, etc.) after glutamate or saline control, from the same experiments as B. There were significant overall effects of anisomycin (F[1,36] = 8.69, p<0.01), the glutamate x anisomycin interaction (F = 3.87, p<0.05), and the anisomycin x history interaction (F[14,504] = 2.26, p<0.01) in a 3-way ANOVA with one repeated measure (history).