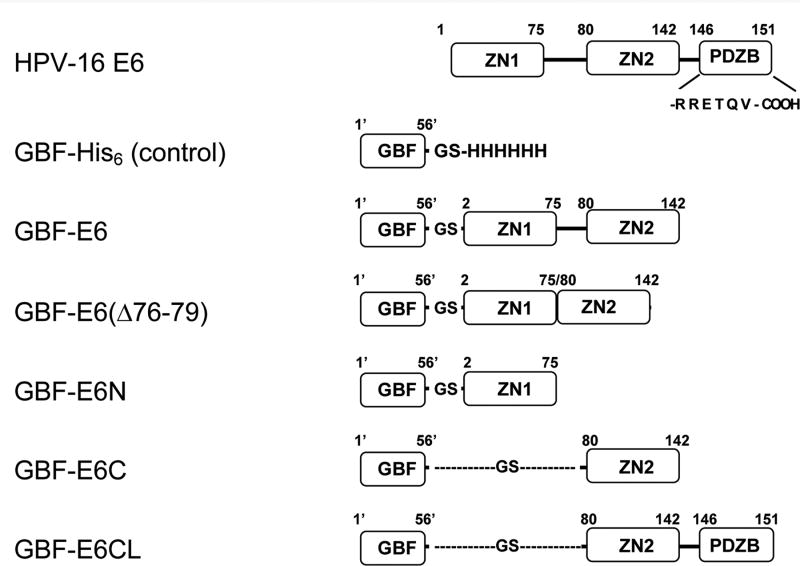
Figure 1.
The E6 constructs used in this study. The E6 protein has two zinc-binding domains (ZN1 and ZN2) and a PDZ-binding motif (PDZB). The residues of the PDZ-binding motif, RRETQV, are indicated. The residues of GBF are numbered as 1′ to 56′. GBF-E6 comprises F2Q3D4…S140R141S142 of wild-type HPV-16 E6 with 4 Cys to Ser mutations at 80, 97, 111 and 140); GBF-E6(Δ76-79) comprises F2Q3D4…S140R141S142 with the same 4 Cys to Ser mutations, but without Y76R77H78Y79; GBF-E6N comprises residues F2Q3D4…I73S74E75 of wild-type HPV-16 E6; GBF-E6C comprises residues S80Y81S82…S140R141S142 of wild-type HPV-16 E6 with the 4 Cys to Ser mutations; GBF-E6CL comprises residues S80Y81S82…T149Q150V151 with the 4 Cys to Ser mutations. GBF-E6 and GBF-E6C constructs with a Trp to Phe mutation in the GBF region (W43′F) were also prepared.