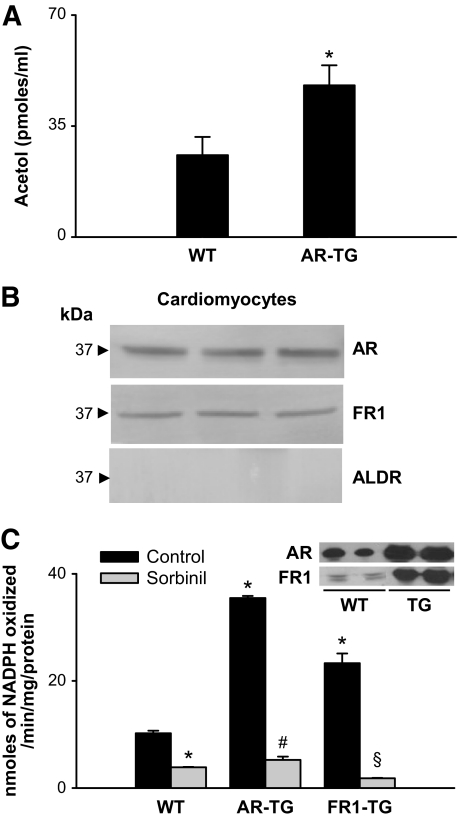
FIG. 3.
AKR-catalyzed reduction of methylglyoxal in mouse heart. A: Acetol generated in effluents of isolated wild-type (C57) or aldose reductase–transgenic hearts perfused with 20 μmol/l methylglyoxal. Acetol concentration was measured by GC-MS after derivatization with PFBHA and BSTFA. 13C3 Acetol was used as an internal standard. Data are presented as means ± SE. *P < 0.01 vs. wild type (n = 4). B: Western blot analysis of cardiac myocytes isolated from adult male C57 mice probed with antibodies raised against AKR1B1 (aldose reductase), AKR1B8 (FR-1), and AKR1A4 (ALDR). Figure shows bands from three different mice. C: Rate of methylglyoxal reduction in homogenates prepared from hearts of wild-type mice (n = 6) or mice with cardiac myocyte–specific transgene expressing AKR1B4 (rat aldose reductase; n = 6) or AKR1B8 (FR-1; n = 6). The enzyme activity was determined with 1 mmol/l methylglyoxal and 0.15 mmol/l NADPH, with or without 1 μmol/l sorbinil. Inset shows Western blots from wild-type and transgenic hearts developed with anti–aldose reductase and anti–FR-1 antibodies. *P < 0.01 vs. wild type (control), #P < 0.01 vs. aldose reductase–transgenic (control), and §P < 0.01 vs. FR1–transgenic (control). AR-TG, aldose reductase–transgenic; WT, wild type.