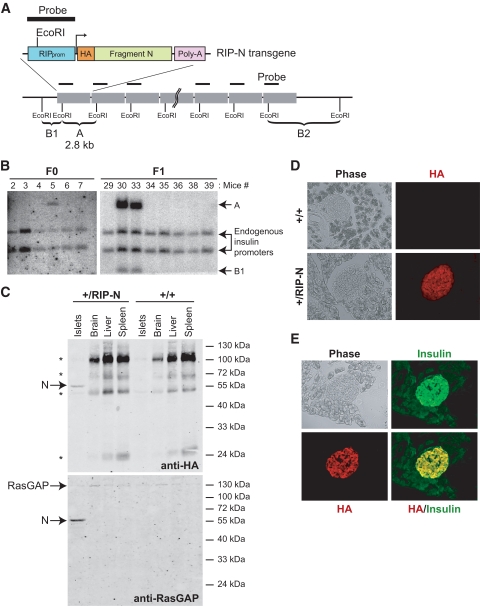
FIG. 1.
Expression and function of fragment N in RIP-N mice. A: Schematic representation of the RIP-N transgene together with the strategy for its detection by Southern blot. An HA-tagged form of fragment N (amino acids 1–455 of RasGAP) followed by an SV40-derived poly-A sequence was placed under the control of the RIP. Band A corresponds to the transgene-specific EcoRI Southern blot fragment. B1 and B2 are examples of EcoRI Southern blot fragments derived from random insertions of the transgene into the host's genome. B: Identification of RIP-N transgenic mice. The progeny of the injected pseudo-pregnant mice were genotyped by Southern blot (see research design and methods for details). Band A (2.8 kb) is specific for the transgene. Founder 1 (mouse 5) was able to transmit the transgene to the F1 generation. C: Tissue expression of fragment N. Lysates from the indicated tissues were analyzed for the presence of fragment N by Western blot using anti-HA and anti-RasGAP antibodies. D: Expression of fragment N in the pancreas. The presence of fragment N was assessed by immunofluorescense analysis of paraformaldehyde-fixed cryosections using an antibody recognizing the HA tag borne by fragment N. E: Colocalization of insulin and fragment N. The specific location of fragment N in pancreatic β-cells was determined by immunofluorescence of paraformaldehyde-fixed cryo-sections from RIP-N mice using anti-insulin and anti-HA antibodies. (A high-quality color digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)