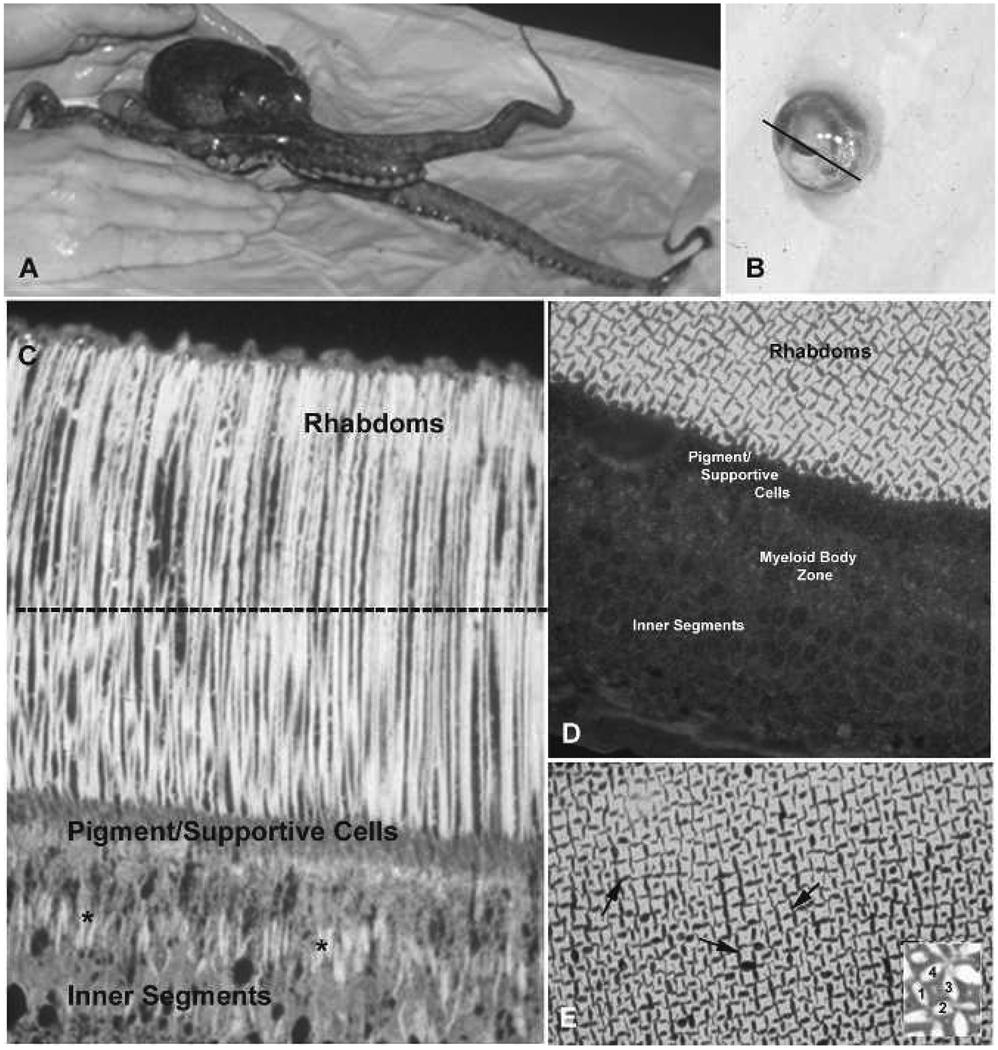
Figure 1.
Retinal structure in Octopus bimaculoides. A, O. bimaculoides. B, Dissected eye from O. bimaculoides. Line through the iris marks the plane of sectioning, after removal of the iris and lens, to obtain retinal image shown in C. C, Longitudinal section through retina showing photoreceptor structure. The dotted line indicates plane of sectioning to obtain tangential to cross-sections through rhabdoms shown in D–E. D, Tangential section through retina to show details of rhabdom structure. E, Arrows highlight individual rhabdoms. In the inset, 1–4 denote the cytoplasm of four individual cells. Each side of the cells contributes one rhabdomere, composed of microvilli, which form the rhabdom.