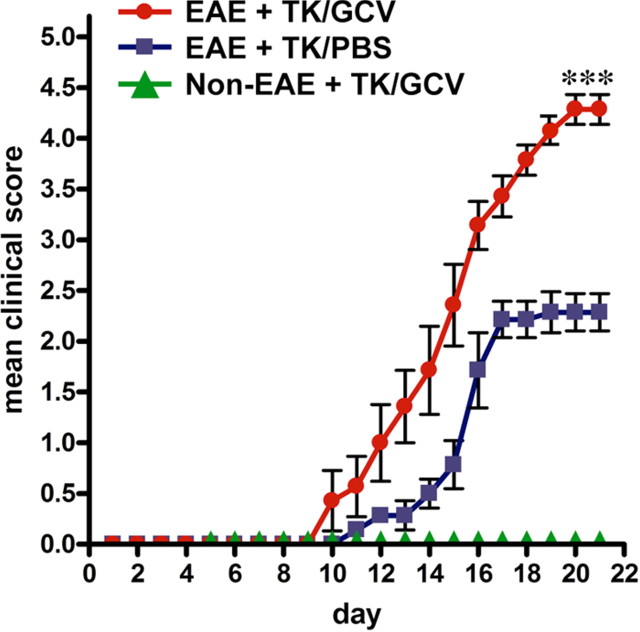
Figure 2.
Exacerbated clinical signs of EAE in mice with transgenically targeted ablation of proliferating reactive astrocytes. Graph showing observer scored clinical rating scale (mean ± SEM) of EAE signs in GFAP-TK transgenic mice that were induced with EAE and given either PBS (EAE+TK/PBS) as a vehicle control, or GCV (EAE+TK/GCV) to ablate transgene-expressing astrocytes, or GFAP-TK mice given GCV but not induced with EAE (Non-EAE+TK/GCV). GFAP-TK mice induced with EAE and given PBS exhibited a moderately severe clinical course that reached a plateau as expected. GFAP-TK mice induced with EAE and given GCV exhibited a rapidly fulminant clinical course that was significantly more severe than that of mice given PBS. GFAP-TK mice given GCV but not induced with EAE exhibited no clinical signs. Data are representative of two separate experiments. ***p < 0.001 relative to EAE+TK/PBS, ANOVA with post hoc pairwise comparisons; n = 7 per group.