Figure 2.
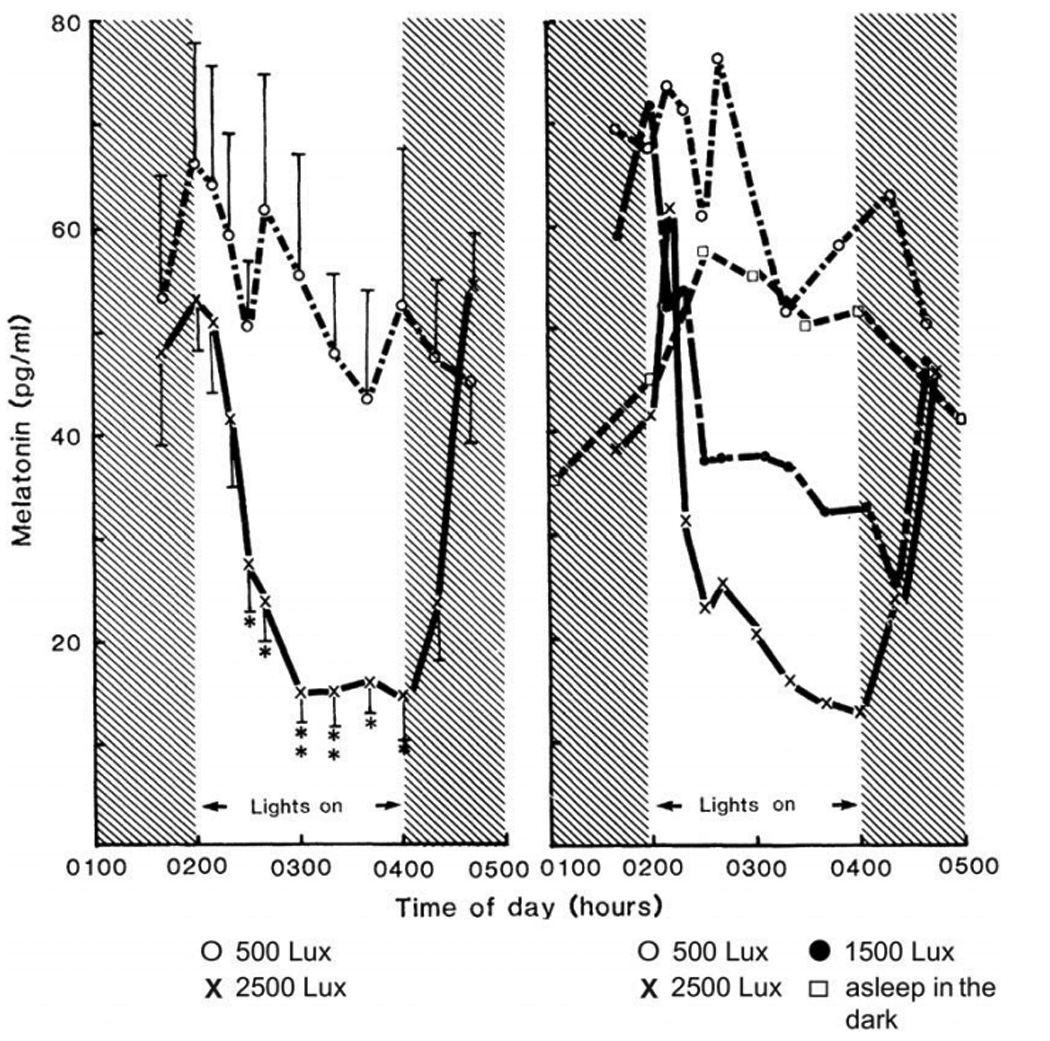
Figure 2 (left). Effect of light on melatonin secretion. Each point represents the mean concentration of melatonin (+/− standard error) for six subjects. Figure 2 (right). Effect of different light intensities on melatonin secretion. The averaged values for two subjects are shown. Symbols: (O) 500 lux; (X) 2500 lux;
(●) 1500 lux; and (□) asleep in the dark. Melatonin levels were measured by mass spectrometry [13]. These early studies were responsible for an increased awareness of the importance of the light/dark cycle as a zeitgeber (time cue) for human circadian rhythms and for the use of the dim light melatonin onset (DLMO) as a circadian phase marker and of bright light as a circadian phase resetting agent in the treatment of circadian phase disorders, including winter depression (SAD) and the circadian disorders experienced by totally blind people. From [21], with permission.
