Figure 2. Cdk3 interacts with and phosphorylates ATF1 in vitro and ex vivo.
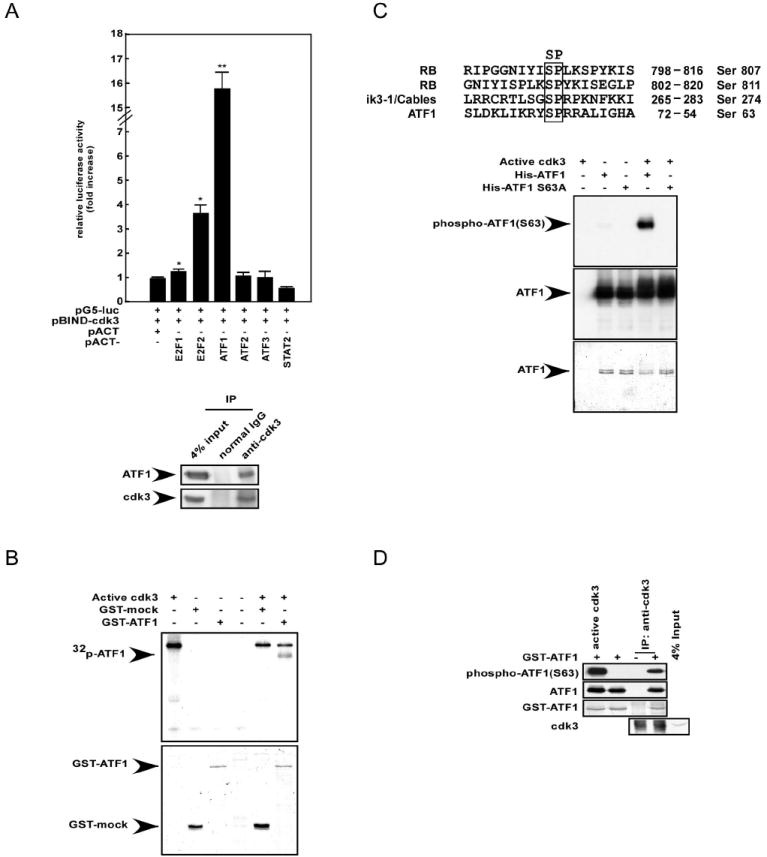
(A, top) The mammalian two-hybrid assay was performed using HEK293 cells to assess the ex vivo protein–protein interaction of pBIND–cdk3 with various pACT–transcription factors (TFs). Activity is expressed as relative luminescence units normalized to a negative control (value for cells transfected with pG5-luc/pBIND-cdk3/pACT = 1.0). The firefly luciferase activity was normalized against the Renilla luciferase activity. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. of values obtained from triplicate experiments. Significant differences were evaluated using the Student’s t–test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001). (A, bottom) Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) was performed using T98G cells. Cells cultured in 10% FBS/MEM were harvested and then subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-cdk3 and subsequent Western blotting with antibodies to detect ATF1 or cdk3. (B) A GST-ATF1 fusion protein was used in an in vitro kinase assay with active cdk3 and results were visualized by autoradiography (top panel). Coomassie blue staining indicates the respective GST fusion proteins (bottom panel). (C) His-ATF1 and His-ATF1 S63A fusion proteins were partially purified and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay with active cdk3. Results were visualized by Western blotting with anti-phospho-ATF1 or anti-ATF1. Coomassie blue staining indicates the respective His fusion proteins. (D) T98G cells were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-cdk3. Kinase activity was assayed using GST-ATF1 as a substrate, followed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-ATF1, anti-ATF1, or anti-cdk3.
