Figure 4.
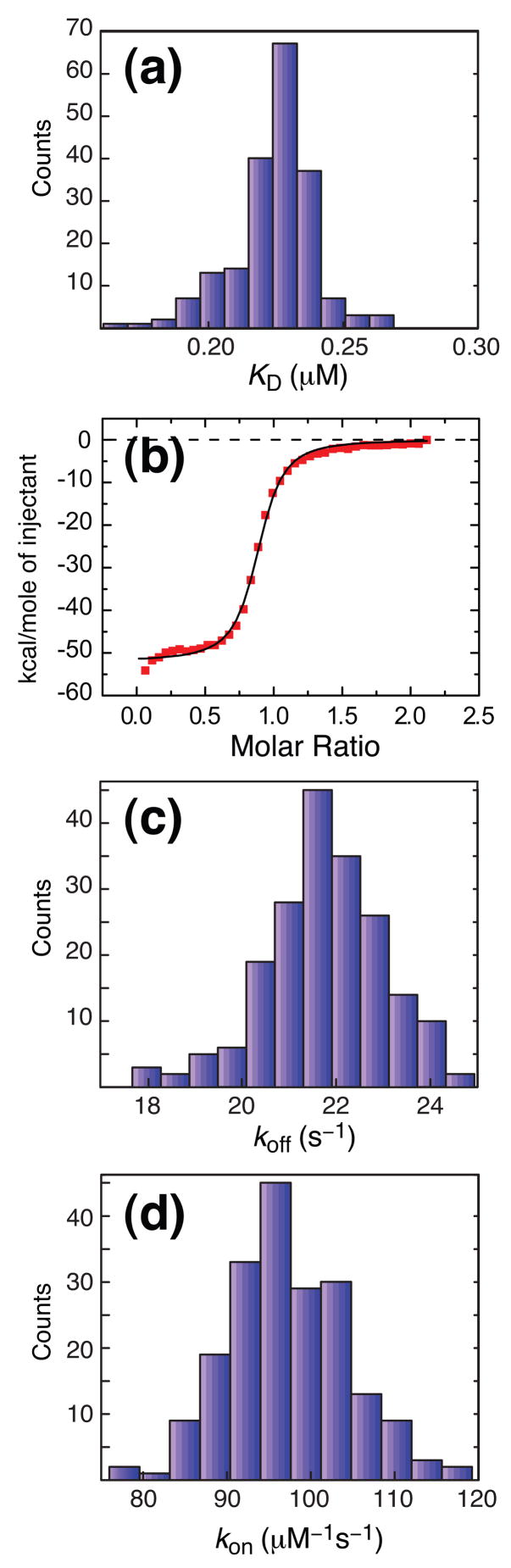
Values of KD, koff and kon for the Chz1, H2A.Z-H2B interaction (35°C) derived from NMR relaxation dispersion data along with ITC titration data for the H2A.Z-H2B/Chz1 binding reaction. The 200 values of {pChz1(i);kex,Chz1(i)}i≤200 and {pH2A.Z- H2B(j);kex,H2AZ.H2B(j)}j≤200 generated from the bootstrap analysis described in the legend to Figure 3 were used to calculate the distributions according to (a) KD(i)= pChz1(i)pH2A.Z-H2B(i)[H2A.Z-H2B]Total, (c) koff calculated using Eq [5] and {pChz1(i);kex,Chz1(i)}i≤200, {pH2A.Z-H2B(j);kex,H2A.Z-H2B(j)}j≤200, while (d) kon was calculated as kon(i)= koff(i)/KD(i). (b) Integrated enthalpy vs. [Chz1]/[H2A.Z-H2B] ratio that is obtained from ITC data recorded at 35 °C. These experiments were preformed using a sample with a single stranded H2A.Z-H2B concentration of 15 μM in a chamber of 1.4 ml. 39 injections (each of 7 μl) of a 200 μM Chz1 solution were made and the heat released analyzed using standard Origin software (http://www.originlab.com) to obtain a KD of 0.10 μM.
