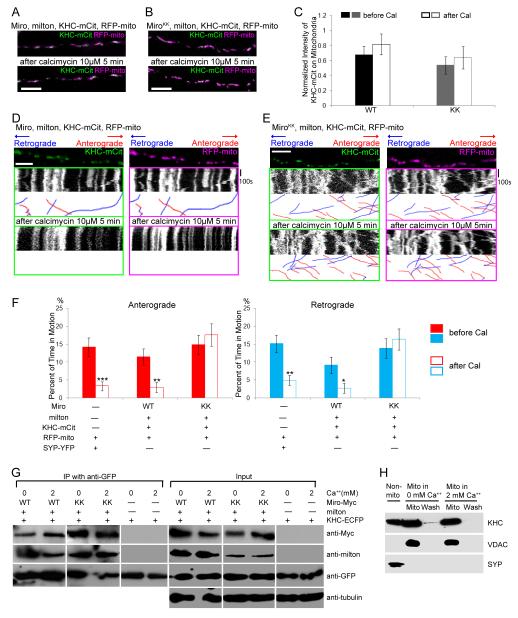
Figure 4. All Axonal Mitochondria Have KHC.
(A, B) In axons transfected with KHC-mCit (green), RFP-mito (magenta), milton, and Miro (A) or MiroKK (B), KHC colocalizes with mitochondria both before and after calcimycin addition. (C) Quantification of the fluorescent KHC present on mitochondria defined by the intensity of mCit in the region overlapping RFP-mito, averaged across 30-31 mitochondria from 3 independent transfections, before and after calcimycin (Cal) application. No significant change in intensity was detected upon calcimycin application (P>0.23 by Mann-Whitney U test). WT, Miro/milton/KHC-transfected neurons; KK, MiroKK/milton/KHC-transfected neurons. (D, E) In kymographs from axons like those in A and B, KHC-mCit and RFP-mito colocalize on stationary mitochondria and move congruently, regardless of the direction of motion, both before and after calcimycin addition. (F) Significant inhibition of movement by calcimycin (Cal) was found in control and Miro/milton/KHC-transfected but not in MiroKK/milton/KHC-transfected neurons. n=144-152 mitochondria from 10 axons and 4 separate transfections. (G) Ca++ does not cause dissociation of the milton/Miro/KHC complex. HEK cells were transfected with Miro or MiroKK together with KHC-ECFP and milton, and lysed in either 5mM EGTA or 2mM Ca++. KHC-ECFP was precipitated with anti-GFP and the precipitate (IP) was assayed. Input lanes were loaded with one fifth the amount of homogenate used for immunoprecipitations, and anti-tubulin was used as a loading control. (H) A mitochondrial enriched fraction from cultured rat hippocampal neurons was separated from other cytoplasmic components (Non-mito), and resuspended in either 0 or 2 mM Ca++ buffer. After centrifugation the pellet (Mito) and supernatant (Wash) were separated by SDS-PAGE and assayed for endogenous KHC, the mitochondrial marker VDAC, and the synaptic vesicle marker SYP. Scale bars, 10 μm.