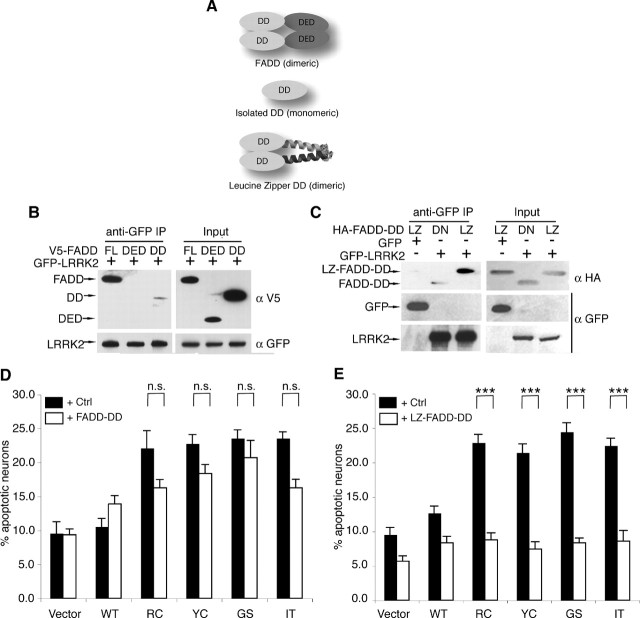
Figure 2.
LRRK2-induced neuronal death requires FADD. A, A schematic depicts the domain structure of FADD, the isolated death domain (FADD-DD), and the leucine-zipper-DD (LZ-FADD-DD) in which the death domain is dimerized through the addition of a leucine zipper. B, FADD interacts with LRRK2 via its DD. GFP-LRRK2 was coexpressed with V5-tagged full-length FADD, FADD-DED, or FADD-DD in 293T cells, and was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP. Copurified FADD or FADD domains were detected by anti-V5 immunoblotting. C, LRRK2-FADD interaction is enhanced by dimerization of FADD-DD. The interaction between GFP-LRRK2 and monomeric (DD) or dimeric (LZ) FADD-DD was assessed by anti-HA after immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP in 293T cells. D, FADD-DD is a poor inhibitor of LRRK2 neurotoxicity. Mouse cortical neurons were transfected with LRRK2 + lacZ (Ctrl) or LRRK2 + FADD-DD. A GFP reporter was cotransfected in each case. Transfected neurons displaying apoptotic nuclear morphology were counted 48 h after transfection using DAPI. Data are the mean ±SEM from three individual experiments of triplicate coverslips (n.s., nonsignificant; ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). E, Dimeric FADD-DD effectively blocks LRRK2 neurotoxicity. Mouse cortical neurons expressing LRRK + lacZ (Ctrl) or LRRK2 + LZ-FADD-DD were assessed as in D (***p < 0.001).