Figure 4.
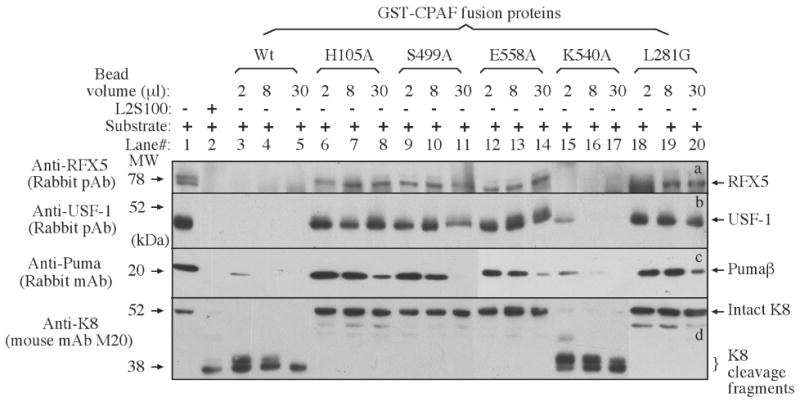
Degradation of target proteins by CPAF mutants in a cell-free assay. Either nuclear extract (NE) containing RFX5 (panel a) & USF-1 (b) or cytosolic extract (CE) containing Puma (c) and keratin 8 (d) were used as substrates to mix with the enzyme source (either L2S100 or various GST-CPAF fusion proteins) and the mixtures were incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. The entire mixture from each reaction was loaded into the corresponding lanes as indicated on top of the figure. After electrophoresis, the resolved protein bands were blotted onto nitrocellulose membrane for corresponding antibody detection as indicated along the left side of the figure. One independent set of enzyme/substrate reactions was used for detecting each substrate. The intact full-length keratin 8 has a molecular weight of 52 kDa and CPAF is known to cleave keratin 8 into 38 kDa fragments [17].
