Fig. 7.
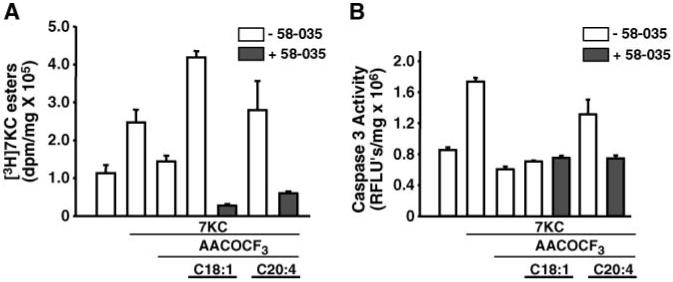
The effect of supplementing arachidonic acid (AA) and oleic acid in the presence of AACOCF3 on the formation of [3H]7KC esters and the induction of caspase-3 activity by 7KC. A: The effect of AA or oleic acid supplementation on AACOCF3 inhibition of [3H]7KC ester formation. P388D1 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of AACOCF3 (20 μM) or 58-035 (10 μg/ml) for 1 h and then supplemented with or without 7KC (10 μg/ml) and either oleic acid or AA (50 μM) complexed to fatty acid-free BSA, as indicated. [3H]7KC (1.0 μCi/ml) was added to the cells, and after a 6 h incubation, the lipids were extracted and the radioactivity incorporated into [3H]7KC esters was determined as described for Fig. 5. B: The effect of AA or oleic acid supplementation on AACOCF3 inhibition of 7KC-induced apoptosis. P388D1 cells were supplemented with or without oleic acid or AA (50 μM) in the presence of either AACOCF3 (20 μM) or 58-035 (10 μg/ml) for 1 h before the addition of unlabeled 7KC (10 μg/ml), as indicated. After a 16 h incubation, the cells were harvested, and caspase-3 activity was determined as described above. FLU, fluorescence light units. Error bars represent standard deviation.
