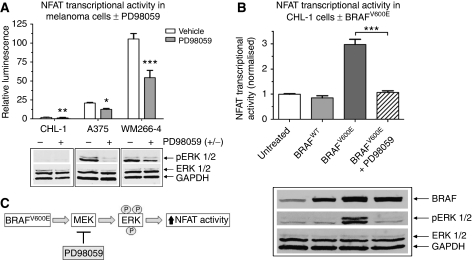
Figure 2.
BRAFV600E activates nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) through a extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK)-dependent pathway. (A) NFAT transcriptional activity was measured 16 h after treatment with the MEK inhibitor PD98059 (10 μM). Values are means from three independent experiments carried out in triplicate (±s.e.m.). Identically treated samples were prepared for western blotting and membranes were probed for phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) (pERK 1/2) and total ERK (ERK 1/2). (B) The effect of BRAFWT or BRAFV600E overexpression on NFAT transcriptional activity in CHL-1 cells was measured by co-transfecting cells with an NFAT luciferase reporter±vectors expressing BRAFWT or BRAFV600E. BRAFV600E-expressing cells were also treated with PD98059 where indicated. Untreated cells were transfected with NFAT reporter plus transfection reagent only and NFAT luciferase activity was measured 48 h later. Values are normalised to the untreated control and are means from four independent experiments carried out in triplicate (±s.e.m.). Identically treated samples were prepared for western blotting to confirm BRAFWT and BRAFV600E overexpression and downstream ERK phosphorylation. Equal protein loading was confirmed by blotting for GAPDH. Statistical analysis performed by t-test (A) or one-way ANOVA (B), ** P⩽0.01, *** P⩽0.001 vs vehicle control. (C) Schematic of BRAFV600E-induced NFAT activation.