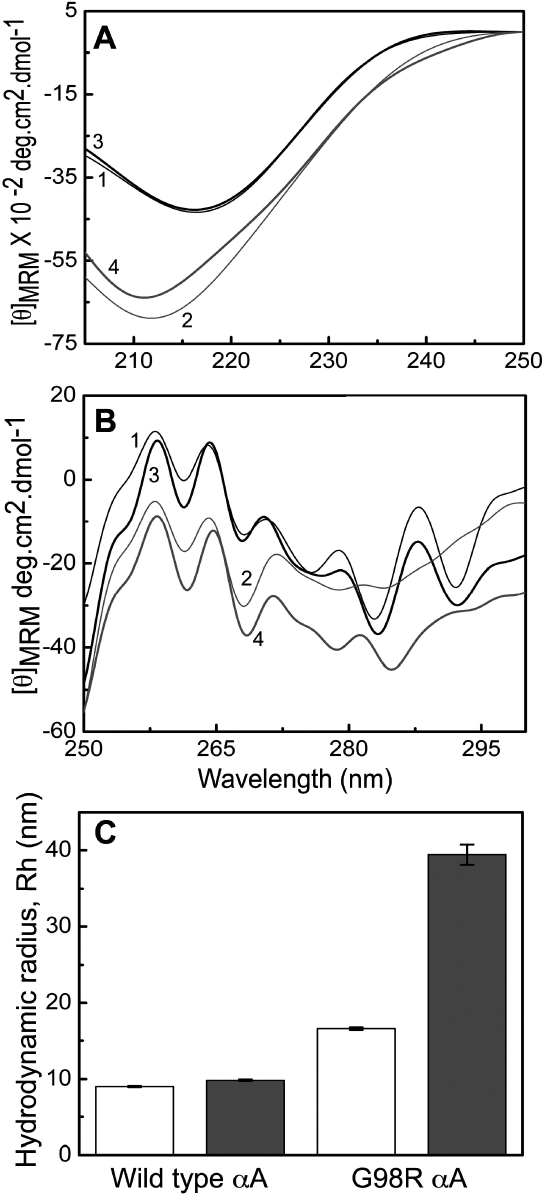
Figure 6.
Cu2+-induced structural changes of αA- and G98R αA-crystallin. Far-UV (A) and near-UV (B) CD spectra of 1 mg/ml of αA-crystallin (curve 1) and G98R αA-crystallin (curve 2) and of 150 μM Cu2+-treated samples of αA-crystallin (curve 3) and G98R αA-crystallin (curve 4) in buffer B are shown. C: Changes in the mean hydrodynamic radii (Rh) of 0.5 mg/ml αA-crystallin and G98R αA-crystallin in the absence (open bars) and in the presence of 75 μM of Cu2+ (filled bars) were determined by dynamic light scattering studies. The error bars represent the statistical variations of the mean hydrodynamic radii of αA-crystallin or mutant αA-crystallin between 10 experimental data. G98R αA-crystallin is more susceptible to the Cu2+-induced structural changes compared to αA-crystallin. [θ]MRM, mean residue mass ellipticity.