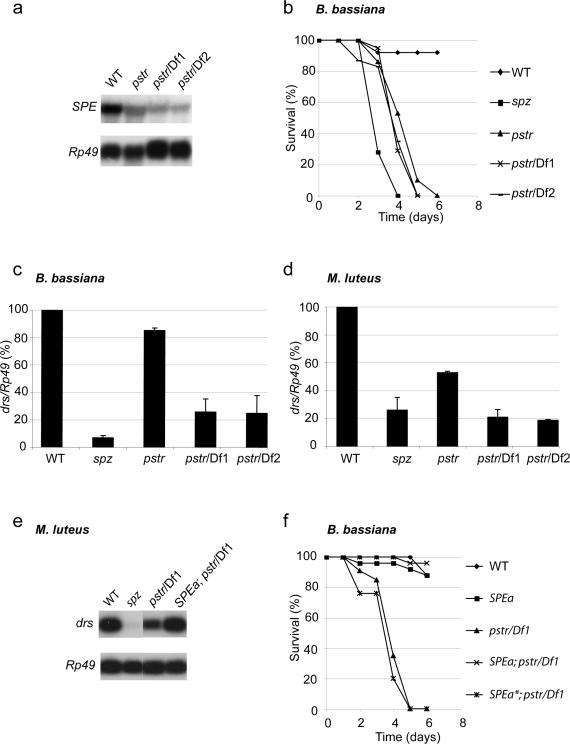
Figure 2. Isolation of the Spaetzle Processing Enzyme (SPE) mutant Pasteur.
(a) Representative RNA hybridization analysis of the SPE gene expression in wild-type (WT), SPEPasteur homozygous (pstr) and SPEPasteur over Df(3R) mbcR1 (pstr/Df1) or Df(3R) mbc30 (pstr/Df2) hemizygous mutant flies.
(b) Survival of adult flies infected by B. bassiana. Genotypes are as in (a).
(c,d) Quantification of RNA hybridization analysis of drosomycin (drs) gene expression, 48 and 24 hours after infection with (c) the fungus B. bassiana and (d) the Gram-positive bacterium M. luteus. Rp49 messenger was used for normalization. drs mRNA expression (drs/Rp49) in wild-type (WT) flies was set to 100 as a control and values obtained with mutant flies were expressed as percentage of this value. Each bar represents the mean of 3 independent experiments, error bars are SD. (c) drs expression is reduced in both SPEPasteur hemizygous mutant flies (P = 0.003 and P = 0,014). (d) drs expression is reduced in all combinations of SPEPasteur mutants (P = 2 × 10-4, P = 2 × 10-5 and P = 3 × 10-5).
(e,f) activated SPE (SPEa) or a catalytically inactive form of this gene (SPEa*) was expressed in SPEPasteur mutant flies using the UAS-GAL4 system under the control of an Actin-GAL4 driver. (e) Representative RNA hybridization analysis of drs gene expression 24 hours after infection with M. luteus. (f) Survival of adult flies infected by B. bassiana.