Figure 5. TB4 alters Marcks expression in vitro and activates PKC in adult epicardium in vivo.
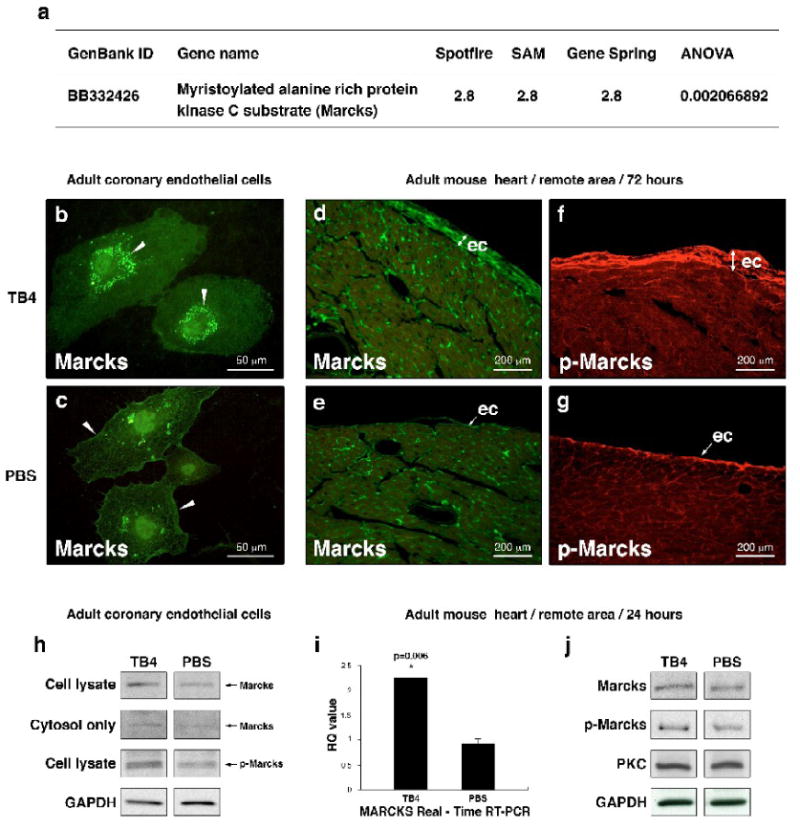
a, cDNA microarray on adult mouse hearts reveals 2.8-fold increase in Marcks expression 24 h after TB4 treatment compared to PBS. i, Real-time RT-PCR of mouse heart RNA confirms the in vitro cDNA microarray results. Bars indicate standard deviation at 95% confidence limits (n=6), *p < 0.05. RQ, relative quantitation assay. b-c, Immunocytochemical analysis of HCECs with Marcks-specific antibody (green) shows increased Marcks expression and translocation from the cell membrane (c white arrowheads) to the cytosol (b white arrowheads) after TB4 treatment (b) suggesting a change in PKC activity by TB4 in vitro. h, Western blot of complete cell lysates and cytosol fractions from adult coronary endothelial cells 24 hours after TB4 or PBS treatment support translocation of Marcks protein into the cytosol and indicate increase in Marcks activation (p-Marcks) by PKC after TB4 treatment in vitro. d-g, Immunohistochemical analysis shows significant increase in Marcks (d,e) and phospho-Marcks (f,g) expressions in thickened epicardium at the intact areas of ligated adult mouse hearts 3 days after TB4 treatment (d,f)). j, Western blot analyses of adult cardiac tissue from the remote areas by Marcks, p-Marcks, PKC, and GAPDH antibodies 24 h after treatment show increase in Marcks expression and phosphorylation without significant change in PKC levels 24 hours after TB4 treatment in vivo (n=6).
