Figure 1. A conserved element in the 3’UTR of HAC1 mRNA is required for splicing in vivo, but not in vitro.
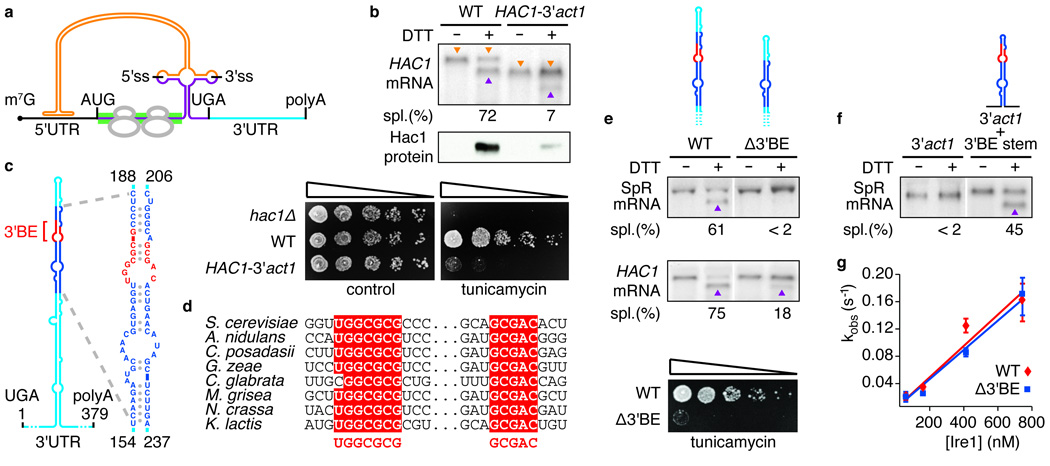
a, Schematic of HAC1 mRNA. The Hac1 ORF is divided into two exons (purple). The intron (orange) base pairs with the 5′UTR (black), causing ribosome stalling (grey). Ire1 cleaves the intron at the indicated splice sites (5′ss & 3′ss). The green bar depicts where the GFP ORF replaces the HAC1 sequence in the splicing reporter. The 3′UTR is indicated in light blue. The 5′cap (m7G), start codon (AUG), stop codon (UGA) and polyadenylation signal (polyA) are indicated. b, e, f, Northern blot of HAC1 or SpR mRNA variants before or after ER stress induction with DTT (10 mM) for 45 min. Purple triangles denote spliced mRNAs; orange triangles denote unspliced mRNAs (only in b). Percent mRNA splicing (“Spl. (%)“) is indicated. Yeast strains harbor a genomic HAC1 copy with its own (WT) or ACT1’s 3′UTR sequence (HAC1-3′act1) (b, top), a genomic copy of SpR (e, top) or HAC1 (e, middle) bearing either the wild-type (WT) or the Δ3′BE mutant 3′UTR, as depicted, or a genomic copy of SpR with the 3’UTR of ACT1 with (3′act1+3′BE stem) or without (3′act1) an insertion of the 64 nucleotide element — shown in expanded view in (c) — as depicted (f). b, middle, Western blot of HA-tagged Hac1 protein from lysates from strains as in (b, top). b,e, Viability assay by 1:5 serial dilutions of hac1Δ or strains as in (b, top) or (e, middle) spotted onto solid media with or without 0.2 µg/ml of the ER stress inducer tunicamycin. Plates were photographed after 3 days growing at 30°C. c, Schematic of the HAC1 3′UTR stem-loop structure with the 3’BE (red) in a region (dark blue) that is shown in expanded view to the right; positional numbering from UGA stop codon. d, alignment of the 3′BE in HAC1 homologues. g, An in vitro intron excision reaction was performed as described8 with Ire1 concentrations: 50 nM, 150 nM, 400 nM, 730 nM of wild-type (red diamonds) or Δ3′BE (blue squares) HAC1 mRNA as substrates.
