Fig. 6.
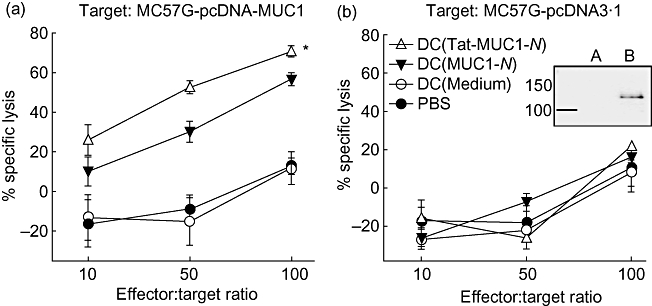
Induction of mucin antigen 1 (MUC1)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Dendritic cells (DCs) (1 × 106 cells) pulsed with either N-terminal region MUC1 (MUC1-N) or Tat-MUC1-N protein were injected twice at weekly intervals into B6 mice (three mice per group). At 7 days after the second immunization, splenocytes were harvested, restimulated with MUC1-N proteins for 3 days and used as effector cells. Effector cells were incubated with MC57G-pcDNA-MUC1 (a) or MC57G-pcDNA3·1 (b). MUC1 expression of target cells was confirmed by Western blot with anti-MUC1 antibody (boxed figure: MC57G-pcDNA3·1 (a) and MC57G-pcDNA-MUC1 (b). After incubation for 4 h, the effector cells and killed target cells were washed off. The target cells that remained in the plates were labelled with [3H]-methylthymidine (5 µCi/ml) for 3 h. [3H]-Methylthymidine uptake was quantified on a microbetacounter. Percentage of specific lysis = [counts per minute (cpm)targets − (cpmtargets+effectors − cpmkillers)]/cpmtargets × 100. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P < 0·05 when compared with DC (MUC1-N).
